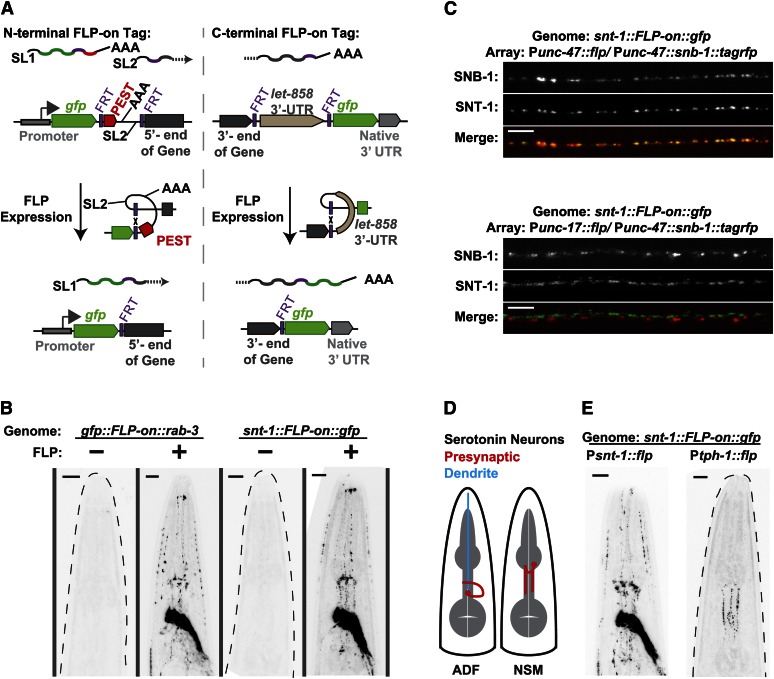
Figure 4.
FLP-on expression of fluorescent tags integrated at native loci. FLP-on::GFP tags were inserted and Cbr-unc-119 was removed as shown in Figure 1A. (A) FLP-on strategies for N-terminal and C-terminal tags. Prior to FLP-based excision, the N-terminal FLP-on connector promotes trans-splicing so that the fluorescent tag and PEST sequence occupy a distinct transcript from the gene transcript. The C-terminal FLP-on connector halts transcription before the fluorescent tag sequence is transcribed. In both cases, FLP expression excises the connector sequence, yielding a single transcript encoding the gene fused to the genetic tag by an FRT-encoded linker. (B) Representative fluorescence images of worms harboring FLP-on::gfp tags fused to either the N terminus of rab-3 or the C terminus of snt-1. FLP was expressed from an extrachromosomal array under the control of the pan-neuronal snt-1 promoter. Dashed gray lines outline worms that did not exhibit fluorescence. Bars, 10 μm. (C) Representative fluorescence micrographs of the ventral nerve cords of snt-1::FLP-on::gfp worms with FLP expressed in different neuronal subtypes. FLP was expressed in either the GABA (Punc-47) or acetylcholine (Punc-17) neurons from stable extrachromosomal arrays. To show cell specificity, snb-1::tagrfp was expressed in the GABA neurons (Punc-47) in both strains. Bars, 5 μm. (D) The serotonin neurons in the C. elegans head, ADF and NSM. Both neurons exist as bilateral pairs; a single neuron is depicted for clarity. Presynaptic regions are shown in red. ADF has a long dendritic process (blue) that does not contain presynapses. (E) FLP activation of snt-1::FLP-on::gfp in the ADF and NSM neurons. FLP was expressed from extrachromosomal arrays under the control of the snt-1 or tph-1 promoters. Bars, 10 μm.