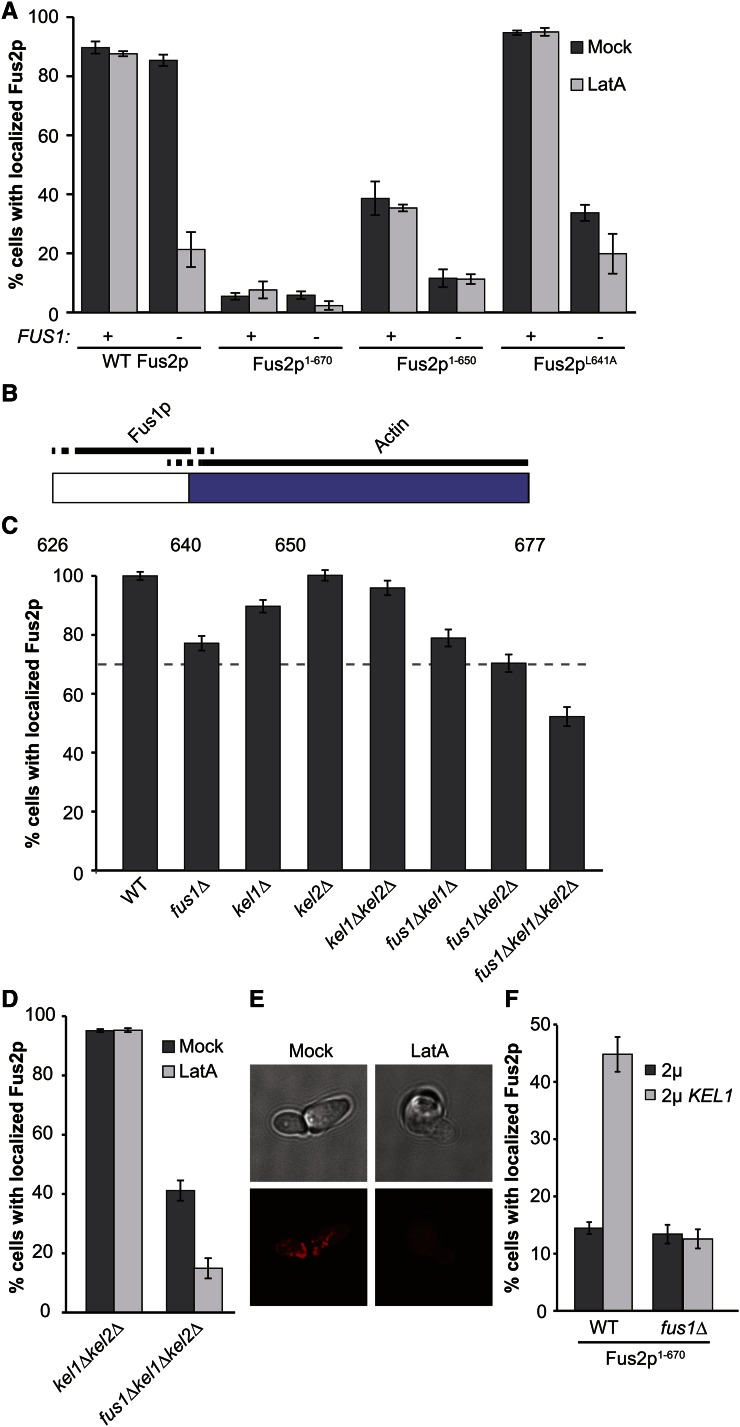
Figure 4.
Fus2p is retained at the shmoo tip via Fus1p- and actin-dependent pathways. (A) The actin-dependent retention pathway acts through the C terminus of Fus2p. Shmoos containing plasmids with FUS2 (pMR5482), fus2-670UAG (pMR6775), fus2-650UAG (pMR6499), or fus2-L641A (pMR6826) were imaged in a fus1∆fus2∆ strain (MY10935) or in a fus2∆ strain (MY10904) after treatment with LatA for 5 min. Control shmoos were mock treated with DMSO. n ≥ 150 shmoos imaged in three independent experiments. (B) Model of where the Fus1p-dependent pathway and the actin-dependent pathway act on the C terminus of Fus2p. Blue shading represents the C-terminal domain required for localization. (C) Kel1p and Kel2p play redundant roles in Fus2p localization. A plasmid containing wild-type Fus2p-GFP (pMR5482) was transformed into strains containing a fus2∆ (MY10904, “WT”) as well as fus1∆ (MY10935), kel1∆ (MY13764), kel2∆ (MY13965), fus1∆kel1∆ (MY13916), fus1∆kel2∆ (MY14545) kel1∆kel2∆ (MY14200), or fus1∆kel1∆kel2∆ (MY14007). Strains were imaged after treatment with pheromone for 1.5 hr. n ≥ 150 shmoos imaged in three or more independent experiments. (D and E) Kel1p and Kel2p act through the actin-dependent pathway. (D) Fus2p localization was assessed in kel1∆kel2∆ (MY14200) and fus1∆kel1∆kel2∆ (MY14339) strains containing pMR5482 and treated with latrunculin A. (E) Actin polymerization was assessed in fus1∆kel1∆kel2∆ via Texas Red-X Phalloidin staining after either mock or latrunculin A treatment. (F) High copy suppression of Fus2p1-670 localization defect by Kel1p is dependent on Fus1p. fus2∆ (MY10904) and fus1∆fus2∆ strains (MY10935) containing fus2-670UAG (pMR6775) were transformed with either high-copy KEL1 (pMR6441) or an empty 2μ plasmid (pRS425). The number of shmoos with localized Fus2p was quantified as before. n> 240 shmoos imaged in 3 independent experiments.