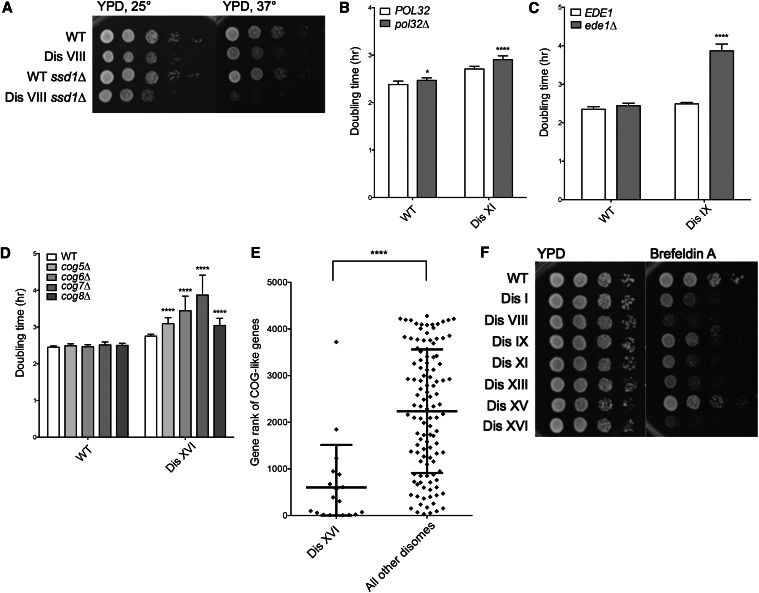
Figure 2.
Karyotype-specific synthetic negative interactions. (A) Cultures of wild-type and disome VIII strains either wild type or deleted for SSD1 were grown overnight in YPD, and 10-fold serial dilutions were plated on YPD plates at the indicated temperatures. (B–D) Doubling times of disomes either wild type or deleted for the indicated genes were determined by growing cells in YPD at 25° and taking OD600 measurements every 15 min over 24 hr. SD is shown. *P < 0.01, ****P < 0.00001; Student’s t-test. (E) Genes that exhibited similar negative synthetic interactions in SGA analyses as the COG5–8 genes were identified using the DRYGIN online database (Koh et al. 2009). The distribution of specific ranks of these genes (CBF1, TLG2, ARL1, IRS4, SYS1, GYP1, RIC1, YPT6, VPS51, VPS63, ERV14, RUD3, YLR269C, GET2, COY1, IMH1, OCA1, ENT4, SEC22) in the disome XVI SGA screen are plotted, as well as the distribution of the ranks of these genes across the other disome SGA screens (****P < 0.0001, Mann–Whitney test). (F) Cultures of wild-type and disomic strains were grown overnight in YPD, and 10-fold serial dilutions were plated on YPD plates with or without 200 μg/ml Brefeldin A. Plates were incubated at 30° for 2 days before images were taken.