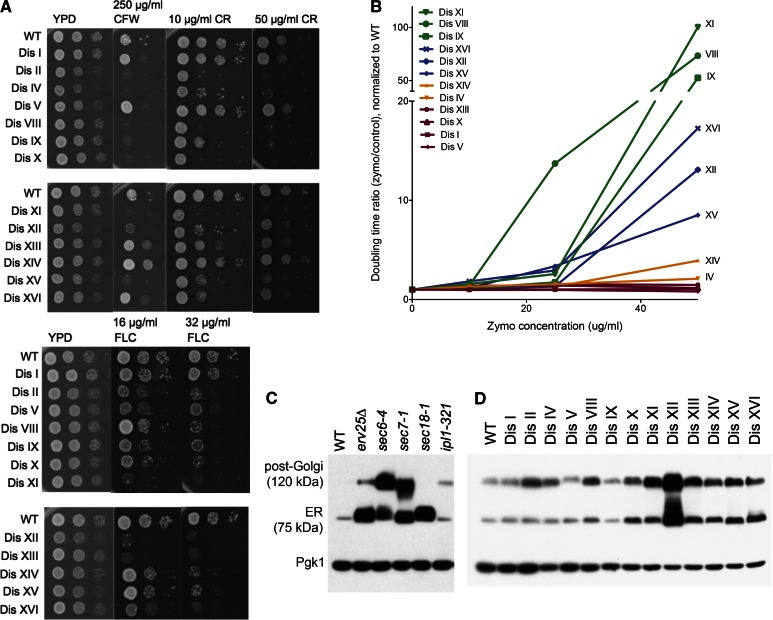
Figure 5.
Protein-trafficking defects are widespread among disomic yeast strains. (A) Wild-type and disomic cells were grown in YPD overnight. Tenfold dilutions were spotted on YPD plates containing the indicated concentrations of CFW, CR, or fluconazole (FLC). Plates were incubated for 2 days at 30° before images were taken. (B) Zymolyase sensitivity was assayed by performing doubling time measurements in YPD ± the indicated concentrations of zymolyase (20T), as described in Figure 2. The ratio of doubling time in the presence of zymolyase to doubling time without the enzyme is plotted as a function of zymolyase concentration, normalized to wild type. (C and D) Cells were grown to mid-log phase in YPD medium at room temperature, and total protein was extracted by trichloroacetic acid precipitation. In the case of the ipl1-321 strain, the culture was shifted to 30° for 3 hr before sampling. Samples were run on SDS-PAGE, and Ccw14p mobility was analyzed by Western blot analysis. The ER and post-Golgi forms of the protein are indicated. (C) Known secretory mutants display accumulation of the protein at predictable points in the secretory pathway and are shown for comparison. Pgk1 is shown as loading control.