Fig. 6.
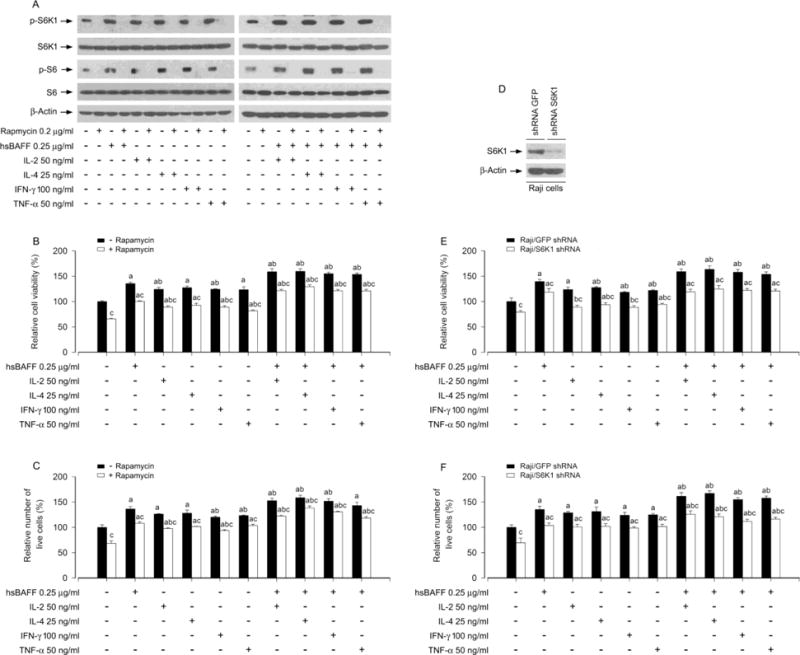
Pharmacological inhibition of S6K1 or down-regulation of S6K1 blocks hsBAFF-stimulated B-cell viability/survival enhanced by IL-2, IL-4, IFN-γ, or TNF-α. Raji cells, or Raji cells infected with lentiviral shRNAs to S6K1 and GFP, respectively, were pre-incubated with/without rapamycin (0.2 μg/ml) for 2 h and then treated with/without hsBAFF (0.25 μg/ml) in the presence or absence of IL-2 (50 ng/ml), IL-4 (25 ng/ml), IFN-γ (100 ng/ml) or TNF-α (50 ng/ml) for 12 h (for Western blotting) or 48 h (for cell viability/survival assay). (A and D) Total cell lysates were subjected to Western blotting using indicated antibodies. The blots were probed for β-actin as a loading control. Similar results were observed in at least three independent experiments. (B and E) Cell viability was monitored by MTS assay. (C and F) Relative number of live cells was estimated by trypan blue exclusion assay. Results are presented as mean ± S.E. (n = 5). ap < 0.05 difference with control group; bp < 0.05, difference with 0.25 μg/ml hsBAFF group; cp < 0.05 − Rapamycin group vs + Rapamycin group or S6K1 shRNA group vs GFP shRNA group.
