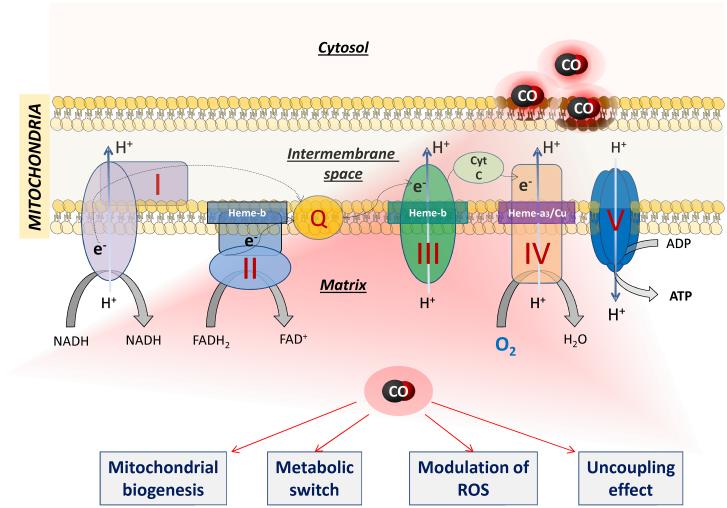
Figure 3. Interaction of CO with mitochondria.
CO at high concentrations is known to inhibit mitochondrial respiration by competing with oxygen for the binding to cytochrome c oxidase (complex IV). In contrast, controlled delivery of CO gas and CO-RMs at non-toxic concentrations can protect cardiac tissue by promoting mitochondrial biogenesis, uncoupling activity and metabolic switch (see text for details). The molecular mechanism(s) underlying these effects remains to be defined. However, the interaction of CO with mitochondrial targets different from cytochrome c oxidase is likely as the electron transport chain contains other heme-complexes that may display distinct sensitivities to CO.