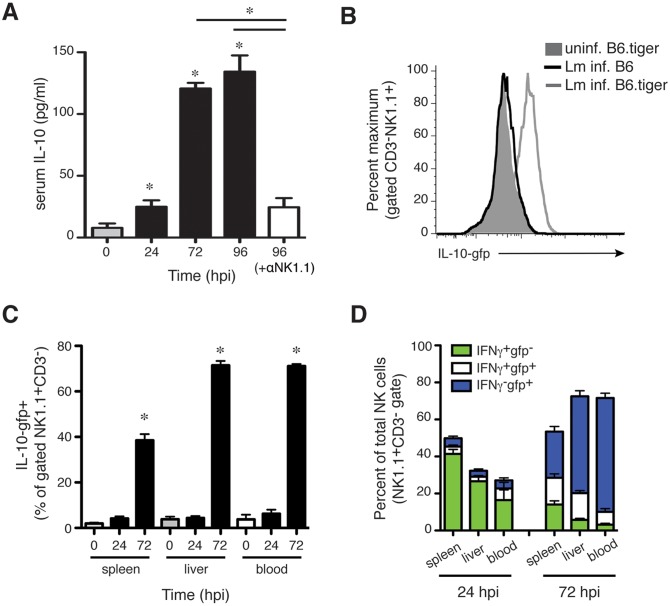
Fig 2. NK cells responding to Lm infection acquire the ability to produce IL-10.
(A) Serum IL-10 concentrations at the indicated times after Lm infection of control IgG2a or αNK1.1 treated B6 mice. Data are pooled from 3 experiments for n = 9–12 mice/group. (B) Histogram depicting the staining for IL-10-gfp reporter in gated CD3-NK1.1+ NK cells from livers of uninfected IL-10-gfp+ (B6.tiger) mice or B6.tiger and control B6 mice at 72 hpi with Lm. (C) Shown are mean ± SEM percentages of gated CD3-NK1.1+ cells that stained positive for IL-10-gfp prior to infection or at 24 or 72 hpi with Lm. Gated NK cells from spleen, liver, and blood of B6.tiger mice were analyzed. Data are pooled from 3 experiments and represent n = 9–14 mice per time point. (D) Proportions of IFNγ+ and IL-10+ populations of NK1.1+CD3- gated NK cells from the indicated tissues at 24 or 96 hpi. Data are pooled from three experiments with n = 3–5 mice/group. Pooled from three experiments representing n = 9–12 mice/group. *P< 0.05 as determined by (A, C) ANOVA.