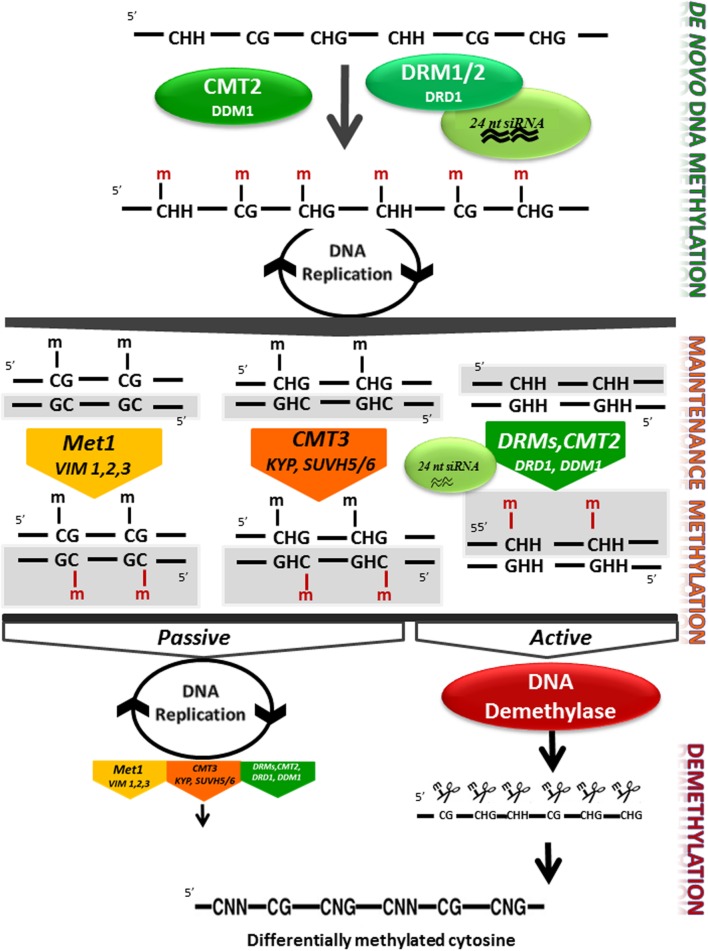
FIGURE 2.
DNA methylation control in plants. Methyltransferases and DNA demethylases are involved in 5mC de novo methylation, maintenance methylation, and demethylation in higher plants. De novo DNA methylation is set up by the RNA directed DNA Methylation (RdDM) pathway involving the DRM1/2 methyltransferases, DRD1 and 24 nt long small RNAs, and by the chromomethylase CMT2 with DDM1 in the CHH sequence context at heterochromatic regions (Zemach et al., 2013). Details of the RdDM pathways are shown in Figure 3. After replication, newly produced DNA will be hemi-methylated at CG and CHG symmetrical sites, but at CHH sites one of the two newly synthesized DNA molecules will not be methylated. Maintenance methylation in the CG context depends on MET1 and VIM1, 2 and 3, and maintenance in the CHG context is catalyzed by CMT3. CHH methylation maintenance depends both on the RdDM pathway and on CMT2 activity. Both CMTs are dependent on histone methylation mediated by KYP and SUVH5 and 6. DNA demethylation can occur passively in a replication dependant way, when the methylation machinery is not or poorly active. 5mC cytosine can be actively removed by DNA glycosylase lyase independently from DNA replication. Newly synthesized DNA strands are highlighted in gray Enzymes names are based on the Arabidopsis model. DRM1/2, CMT2/3 (CHROMOMETHYLASE 2/3), MET1 (cytosine-DNA-methyltransferase 1), VIM1–3 (VARIANT IN METHYLATION 1–3), KYP/SUVH4 [KYP/Su-(var)3–9 homolog 4], SUVH5/6 [Su-(var)3–9 homolog 5/6], DRD1 (DEFECTIVE IN RNA-DIRECTED DNA METHYLATION), DDM1 (DECREASE IN DNA METHYLATION), and 24 nt siRNA (24 nucleotide small interfering RNAs).