Figure 6.
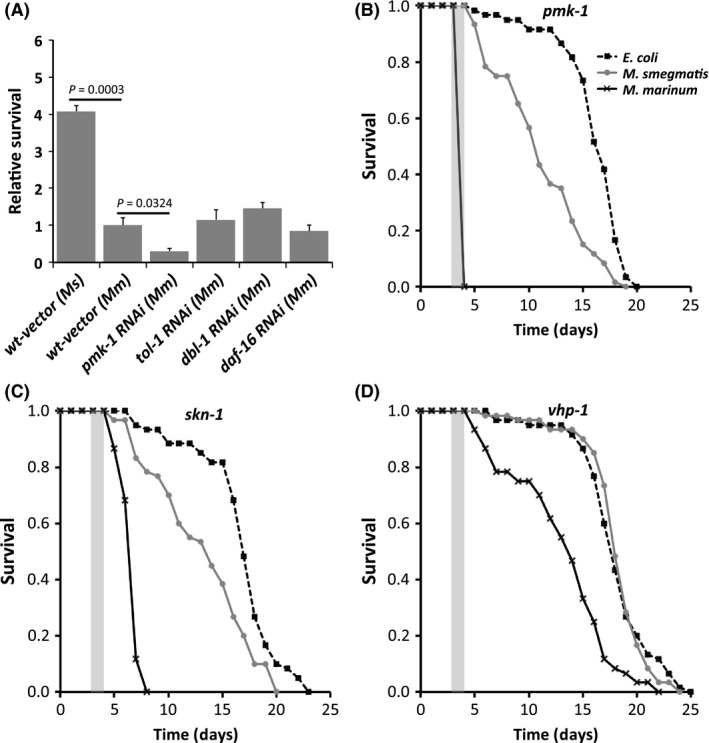
Pathogenic mycobacteria block C. elegans MAPK‐mediated protection using MAPK phosphatase. (A) Relative survival of RNAi knock‐down of p38 MAPK (pmk‐1) TLR (tol‐1), TGF‐ β (dbl‐1) and insulin‐like receptor (daf‐16) at 2 d postinfection as compared with vector alone wild type. Relative survival = number of RNAi knock‐down nematodes surviving/number of wild‐type surviving. Data are means and standard deviations. (B) Survival curve for MAPK (pmk‐1) mutant after 24 h of infection. Mm versus Ms P < 0.0001; Mm versus E. coli P < 0.0001; Ms versus E. coli P < 0.0001. Key in (B) is for (B‐D). (C) Survival curve for the C. elegans the downstream regulator of MAPK (skn‐1) mutant after 24 h infection. Mm versus Ms P < 0.0001; Mm versus E. coli P < 0.0001; Ms versus E. coli P < 0.0001. (D) Survival curve for the C. elegans MAPK phosphatase (vhp‐1) mutant after 24 h infection. Mm versus Ms P < 0.0001; Mm versus E. coli P < 0.0001; Ms versus E. coli P = 0.9173. Survival curve P values from log‐rank analysis.
