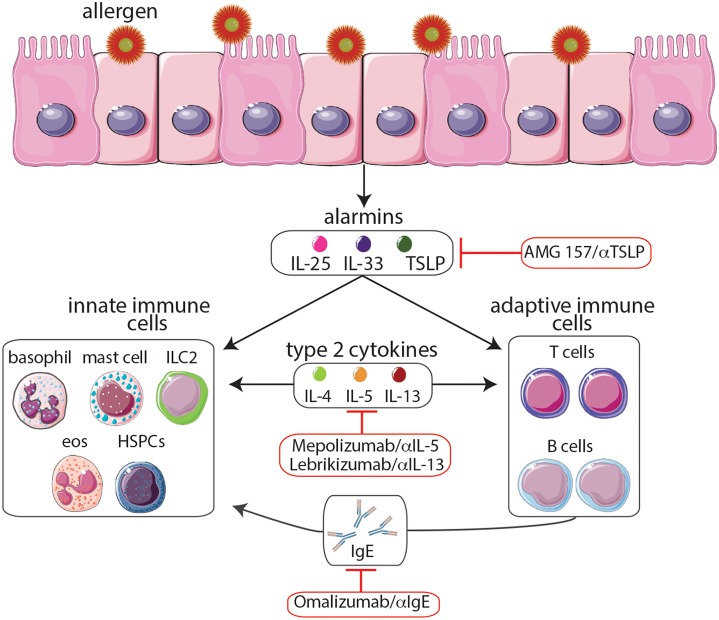
Figure 1.
Following exposure to allergens, epithelial cells release cytokine alarmins including thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP), IL-25, and IL-33. Cytokine alarmins promote the production of type 2 cytokines (IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13) by immune cells of both the innate and adaptive immune systems. Moreover, crosstalk between these two branches further promotes TH2 cytokine-mediated inflammation including production of IgE and the expansion of eosinophil populations, events that contribute to asthma pathogenesis. The anti-IgE monoclonal antibody omalizumab and the anti-IL-5 monoclonal antibody mepolizumab, the only biologics which have been approved by the FDA, provide effective long-term control and reduce the steroid requirement in patients with severe allergic asthma. Moreover, biologics targeting TSLP and IL-13 are currently undergoing clinical trials. Although biologics targeting the cytokine alarmins IL-25 and IL-33 have shown promise in murine studies, further studies are needed to determine their therapeutic potential. The development of biologics to treat allergy-associated asthma will aid in the eventual goal of creating novel personalized treatment regimens.