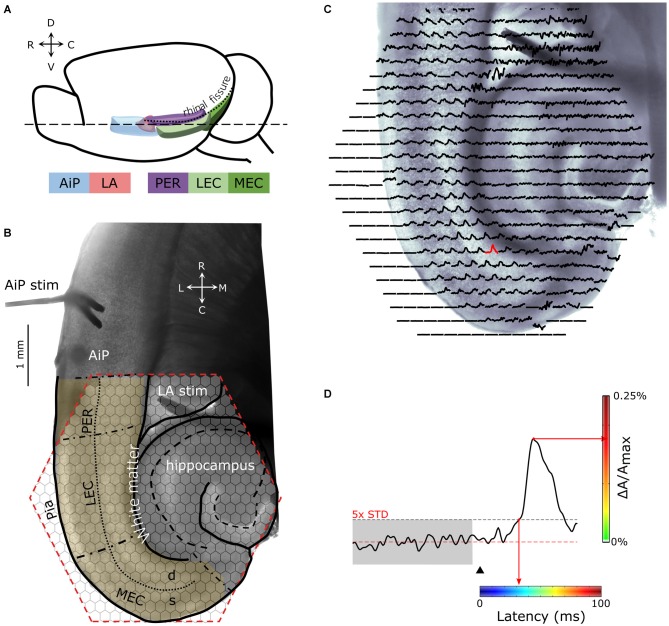
Figure 1.
(A) Schematic drawing of the lateral view of the mouse brain showing the structures of interest. (B) Example of a 400 μm thick horizontal brain slice obtained at the level dashed line (- - -) indicated in (A). Stimulation electrodes were placed in the agranular insular cortex (AiP; neocortical area) and the lateral amygdala (LA), indicated by “AiP stim” and “LA stim”, respectively. The anatomical borders of the perirhinal (PER), lateral EC (LEC), and medial EC (MEC) are indicated with black, dash-dotted lines. The border between the deep and superficial layers in the PER, LEC and MEA is indicated with a dotted line. The cell layers of the hippocampus are indicated with a dashed line. The hexagonal shaped area of the 464-channel photodiode array overlying the PER, LEC and MEC is indicated in red. Neuronal activity was recorded in the region of interest (yellow shaded region). (C) Spatial overview of optical recording with 464-channels of a parahippocampal—hippocampal slice preparation stained with the voltage-sensitive dye NK3630. Each trace represents membrane potential changes of a population of neurons recorded by the channel in response to stimulation in the AiP. (D) Example trace of the evoked response recorded in a single channel in the MEC (the red response in C). The arrowhead indicates the time of stimulation. The red line marks the baseline signal, the gray shaded and the black dotted line area shows the 5× SD over 100 ms of baseline, which is used as the threshold for response latency determination. For spatial representation of the response latency in every channel, the latency was converted to a color-coded scale, in which blue codes the smallest and red the largest latency. The amplitude of the signal (ΔA/Amax) in percentage is color coded from green (0%) to red (0.25%) as indicated with the vertical colorbar to visualize the magnitude of the response at a single time point. Abbreviations: AiP, Agranular insular cortex; LA, Lateral amygdala; PER, Perirhinal cortex; LEC and MEC, Lateral and medial entorhinal cortex; d, Deep layers; s, Superficial layers; C, caudal; D, dorsal; L, lateral; M, medial; R, rostral; V, ventral.