Fig. 2.
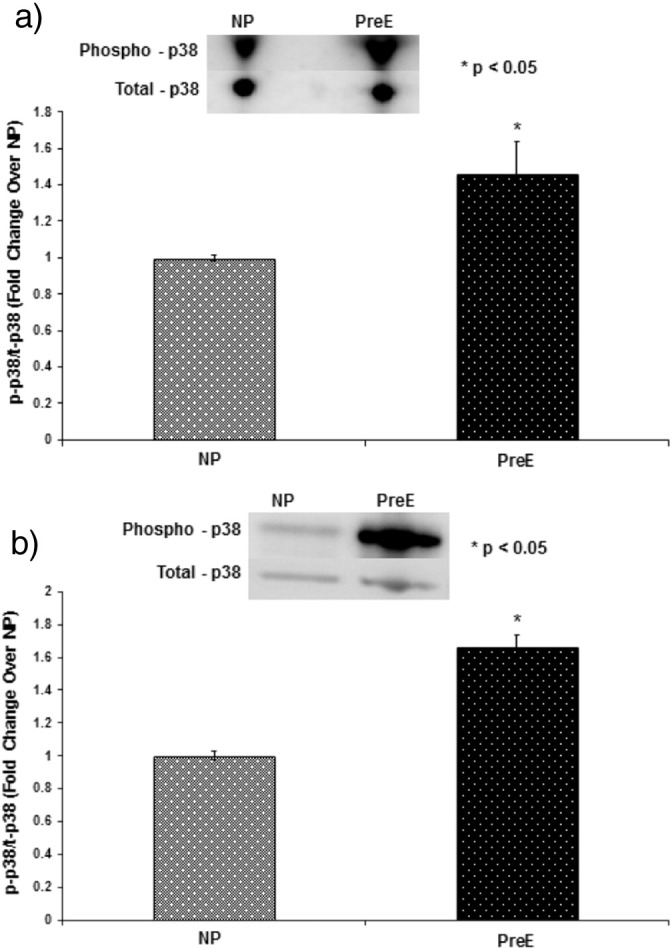
(a) The p38 MAPK phosphorylation was measured in the placental tissue from two groups of patients by Western blotting, running the homogenate from the placental tissues from NP and preE patients in gel followed by detecting with immunoblotting using anti-phospho-p38/anti-total-p38 antibodies. The patients were: normal pregnant (NP, n = 15) and preeclamptic (preE, n = 15). The placental p38 MAPK phosphorylation was significantly upregulated in preE patients compared to NP (*p < 0.05). The results presented are the mean ± SE. A blot from a representative experiment is shown in the figure. (b) The p38 MAPK phosphorylation was measured in the umbilical cord tissue from two groups of patients by Western blotting, running the homogenate from the cord tissues from NP and preE patients in gel followed by detecting with immunoblotting using anti-phospho-p38/anti-total-p38 antibodies. The patients were: normal pregnant (NP, n = 15) and preeclamptic (preE, n = 15). The cord p38 MAPK phosphorylation was significantly upregulated in preE patients compared to NP (*p < 0.05). The results presented are the mean ± SE. A blot from a representative experiment is shown in the figure.
