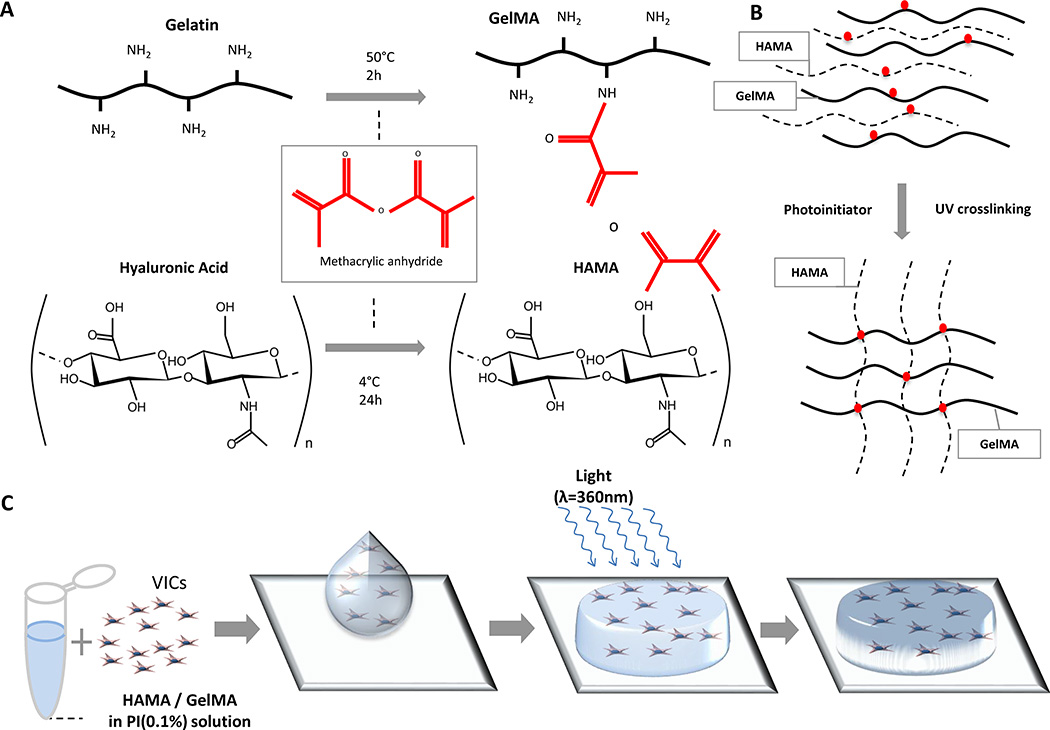
Figure 1. Fabrication of VIC-laden hydrogels.
A, Methacrylation of gelatin (GelMA) and hyaluronic acid (HAMA), respectively, occurs by the addition of methacrylic anhydride groups to dissolved gelatin and hyaluronic acid. B, Schematic depiction of photocrosslinking GelMA and HAMA. By dissolving HAMA and GelMA into a solution containing a photoinitiator, when exposed to UV light, the polymers form crosslinks between the methacrylate groups, creating an ECM-like mesh. C, Schematic depiction of fabricating VIC-laden hydrogels. (1) VICs are isolated from culture and resuspended into a photoinitiator solution containing dissolved 1%(w/v) HAMA and 5% (w/v) GelMA; (2) Cell-polymer suspension is pipetted on to a plate between two spacers (450 µm) and (3) exposed to light at an intensity of 2.5 mW/cm2 for 30 seconds (λ=365 nm), which yields a (4) crosslinked VIC-laden hydrogel disc. VIC-laden hydrogels are then cultured for up to 21 days.