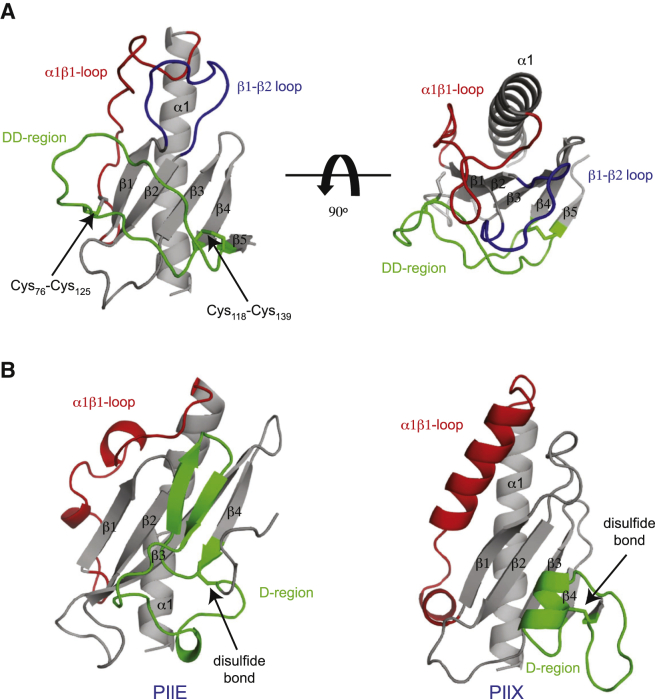
Figure 3.
High-Resolution 3D Structure of the DUS Receptor ComP from N. meningitidis
(A) Crystal structure of the soluble portion of ComP at 1.43-Å resolution. Two different views are shown as a cartoon. The conserved core in type IV pilins (the N-terminal α helix and four-stranded antiparallel β sheet) is depicted in gray. Distinctive/key structural features such as the α1β1 loop (red), the large β1-β2 loop (blue), and the DD region delimited by two disulfide bonds that sits on top of the β sheet (green) are also highlighted.
(B) Structural similarity/differences between the soluble portions of ComP, major pilin PilE from N. gonorrhoeae (Parge et al., 1995), and minor pilin PilX from N. meningitidis (Helaine et al., 2007). The distinctive/key structural features shown in (A) are also highlighted using the same coloring scheme.