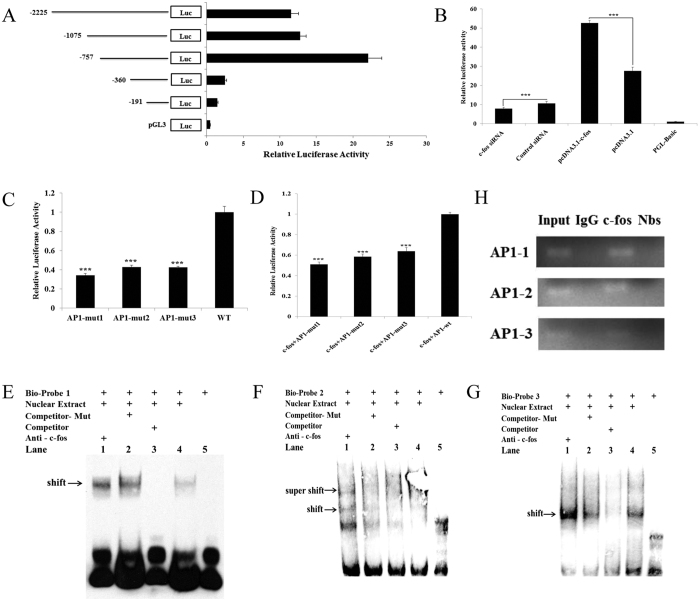
Figure 4. Transcriptional regulation of miR-144.
(A) Identification of miR-144 promoter activity by using luciferase assays in WISH cells. (B) WISH cells were co-transfected with c-fos overexpression vectors and the pGL3-promoter-1075 reporter . The overexpression of c-fos strongly increased luciferase activity. Luciferase activity decreased in WISH cells co-transfected with c-fos siRNA and the pGL3-promoter-1075 reporter. (C) A mutation in the AP-1 binding site strongly reduced transcriptional activity compared with wild-type AP-1. (D) A strong reduction in transcriptional activity was observed in WISH cells cotransfected with c-fos overexpression vectors and the pGL3-promoter-1075 reporter with an AP-1 binding site mutation compared with the reporter with the wild-type AP-1 sequence. (E–G) WISH cells nuclear extracts were incubated with biotin-labelled DNA probes corresponding to the 3 putative AP-1 binding sites in the miR-144 promoter (lanes 2–5). A 200-fold excess of unlabelled DNA probe was included in the reaction to evaluate binding competition. The supershift assay was conducted using an antibody against c-fos (lane 1). (H) ChIP assays using antibodies against c-fos were used to evaluate the binding activity of endogenous c-fos to the region of the AP-1 promoter that contains with the putative c-fos response elements. c-fos binding was evaluated using PCR. The data are presented as the mean ± SEM (*P < 0.05).