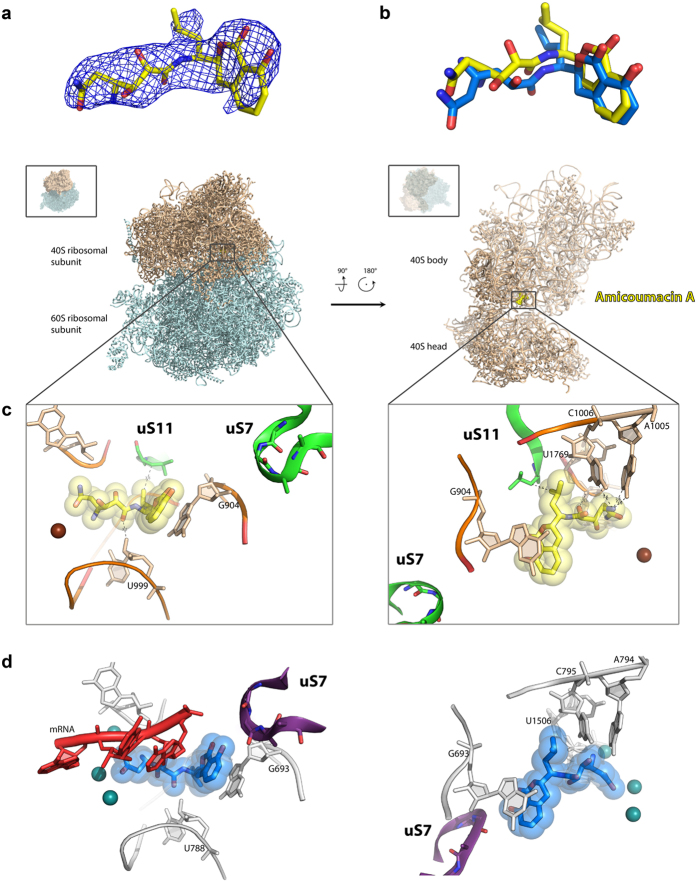
Figure 3. Structure of the amicoumacin A complex with yeast ribosome.
(a) Difference electron density map of amicoumacin A in complex with 80S ribosome. The map is contoured at 2σ. Amicoumacin A is shown in yellow. (b) Comparison of amicoumacin A conformation in yeast 80S and bacterial 70S ribosome. The 70S ribosome from T. thermophilus (PDB entry 4W2F) in complex with amicoumacin A (shown in blue) was aligned on the 80S ribosome based on the helix 23 in 18S or 16S rRNA (ribosomal components are omitted for clarity). (c) The binding pocket of amicoumacin A in small ribosomal subunit E-site. Two orientations of the 80S ribosome in complex with amicoumacin A are shown in the upper panel. The view from the side of the 40S head is shown on the left, and the view from the subunit interface is shown on the right (60S subunit is omitted for clarity). The 40S subunit is colored in wheat, and the 60S subunit is in light blue. The binding pocket of amicoumacin A is magnified in the lower panel. Amicoumacin A is shown in yellow, rRNA residues (in wheat, proteins uS11 and uS7) in green, and magnesium ions in brown. Interactions of amicoumacin A are depicted with the dashed lines. (d) Comparison of the amicoumacin A binding site in a yeast 80S ribosome with the one in bacterial 70S ribosome from T. thermophilus. Amicoumacin A is shown in blue, rRNA residues in grey, protein uS7 in violet, and magnesium ions in dark green (PDB entry 4W2F).