Fig. 1.
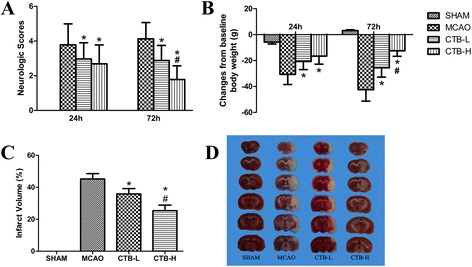
Effect of CTB on neurological deficit scores, body weight, and infarct volume after MCAO. a Elevated neurological deficit scores after MCAO were significantly attenuated by CTB, and neurologic deficits were significantly ameliorated in the CTB-H group compared with the CTB-L group, both at 24 and 72 h. b CTB ameliorated body weight loss at 24 h after cerebral ischemia, while no significant difference was found between the CTB-L group and CTB-H group. At 72 h after cerebral ischemia, body weight loss was significantly ameliorated by CTB, and body weight loss in the CTB-H group was significantly less than that in the CTB-L group. c Quantification of infarct volume at 72 h. The ratio of corrected infarct volume to the nonischemic hemisphere volume was calculated for the cerebral infarct size. Infarct volume was decreased at 72 h with CTB treatment and infarct volume was significantly reduced in the CTB-H group compared with the CTB-L group. d Representative TTC stained brain sections of different groups were shown. Bars represent mean ± SD (n = 8); *p < 0.05 vs MCAO group, and #p < 0.05 vs CTB-L group
