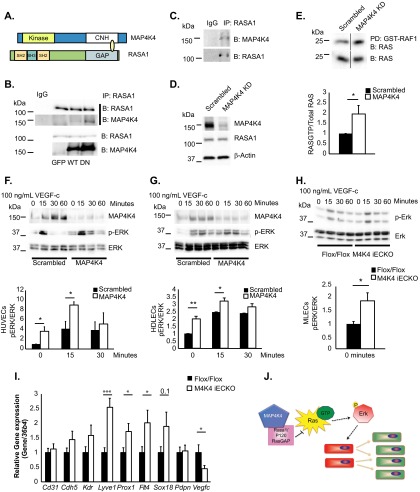
FIG 5.
MAP4K4 binds to RASA1 and regulates basal RAS-ERK signaling. (A) Diagram of MAP4K4 and RASA1 domains that directly bound in a yeast 2-hybrid screen. (B) Coimmunoprecipitation of endogenous RASA1 and overexpressed MAP4K4 in HUVECs. The immunoblots are representative of the results of at least 3 independent experiments. (C) Immunoprecipitation of endogenous RASA1 and endogenous MAP4K4 in HDLECs. The immunoblots are representative of the results of at least 3 independent experiments. (D to G) ECs were treated with scrambled or MAP4K4 siRNA for 48 h. (D) RASA1 protein levels were assessed in HUVECs and normalized to β-actin (representative results; n = 4). (E) Ras-GTP levels were measured in serum-starved HUVECs by assessing GST-RAF1-bound RAS in pulldowns (top) as normalized to total RAS levels in cell lysates (bottom) by densitometry (*, P < 0.05; n = 4). The immunoblots were run on the same gel but in noncontiguous lanes. (F to H) HUVECs (F), HDLECs (G), and MLECs (H) were serum starved overnight and stimulated with 100 ng/ml VEGF-C in a time course. The lysates were immunoblotted for MAP4K4, p-ERK, and total ERK, and p-ERK levels were normalized to total ERK by densitometry (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.005; n = 3 or 4 HUVECs or HDLECs; n = 7 or 8 MLECs). (I) MLECs were isolated from chow-fed Flox/Flox or Map4k4 iECKO mice at least 16 weeks after tamoxifen injections, and the indicated genes were assessed by qRT-PCR and normalized to 36b4 (*, P < 0.05; ***, P < 0.0005; n = 8 to 13). (J) Model of the hypothesis. Map4k4 directly binds Rasa1 to negatively regulate Ras-GTP and Erk activity; thus, Map4k4 loss drives EC proliferation and a lymphatic endothelial cell fate switch, which promotes lymphatic dysfunction. The error bars represent standard errors of the mean.