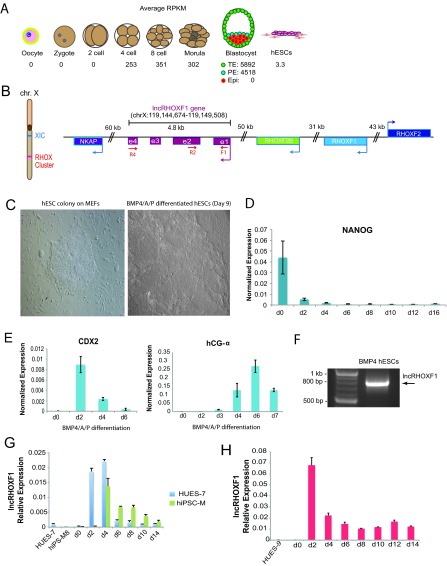
FIG 1.
lncRHOXF1 is robustly expressed during early human development. (A) Schematic showing RNA sequencing reads (RPKM) for lncRHOXF1 during early human development (14). (B) Genomic location of lncRHOXF1 on the X chromosome. XIC, X-inactivation center. Primer locations for transcript cloning (F1 and R4) and qPCR (F1 and R2) are shown. (C) Bright-field images of a human embryonic stem cell colony cultured using mouse embryonic fibroblasts (left) and BMP4/A/P-differentiated cells after 9 days (right). (D) qRT-PCR analysis of decreased NANOG expression during BMP4/A/P differentiation. Error bars denote standard deviations from the means. (E) qRT-PCR analysis of increased placentation markers CDX2 and hCG-α expression during BMP4/A/P differentiation. Error bars denote standard deviations from the means. (F) RT-PCR amplification of exons 1 to 4 of lncRHOXF1 by using primers F1 and R4 and RNA from BMP4/A/P-differentiated hESCs. (G) qRT-PCR analysis of lncRHOXF1 expression in male hESCs (blue) and hiPSCs (green) during BMP4/A/P differentiation. Error bars denote standard deviations from the mean. (H) qRT-PCR analysis of lncRHOXF1 expression during BMP4/A/P differentiation of human female pluripotent stem cells. Error bars denote standard deviations from the means.