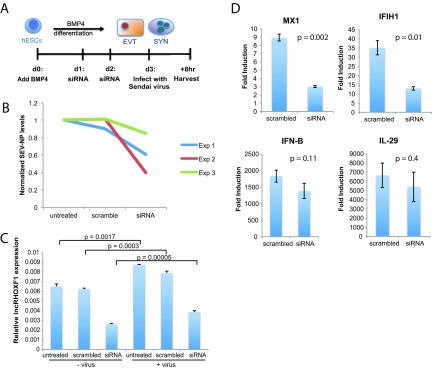
FIG 5.
Sendai virus infection increases lncRHOXF1 expression in human trophophoblast progenitors. (A) Schematic of Sendai virus infection following siRNA-mediated knockdown of lncRHOXF1 RNA during in vitro BMP4/A/P differentiation. (B) qRT-PCR analysis of Sendai virus protein SEV-NP transcript levels in BMP4/A/P-differentiated cells transfected with scramble or lncRHOXF1 siRNAs. Results were normalized to those for untreated controls; results from three independent experiments are shown. (C) qRT-PCR analysis of lncRHOXF1 RNA levels in infected and uninfected BMP4/A/P-differentiated HUES-9 cells. Statistical analysis was determined using a one-tailed t test to compare triplicate measurements of infected versus uninfected cells. Error bars denote standard deviations from the means. (D) Relative expression of each gene was determined in cells treated with mock siRNA (scrambled) or siRNA for lncRHOXF1 RNA by quantifying RNA abundance in cells treated with and without Sendai virus; results were normalized to GAPDH expression results. Relative expression was compared using a two-tailed Welch's t test, and a representative example of 4 independent experiments is shown, as the mean relative expression level, 2(ΔCT [virus] − ΔCT [no virus]) ± the standard deviation.