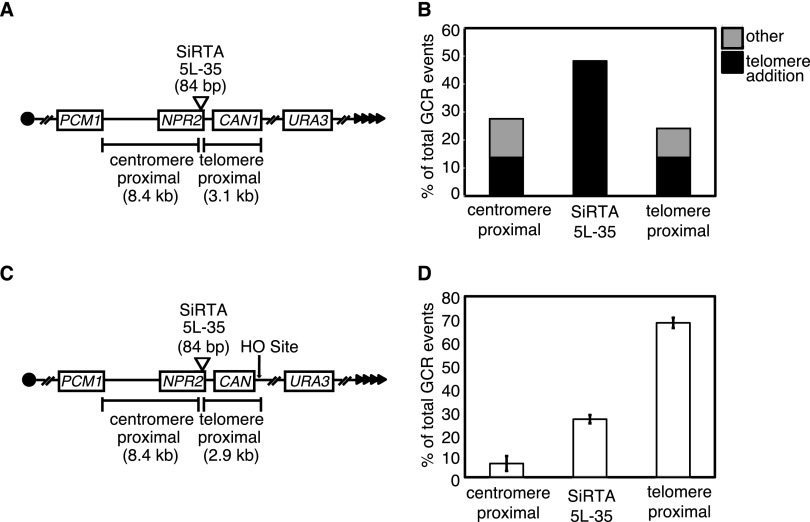
FIG 1.
SiRTA 5L-35 incurs a high frequency of de novo telomere addition relative to flanking sequences. (A) Schematic of chromosome V GCR assay system. Filled triangles represent the terminal telomeric repeats. Throughout the figures, chromosome arms are diagrammed with the telomere to the right. This convention places the 3′ terminus upon which telomerase directly acts on the top strand of DNA. (B) Distribution of spontaneously occurring GCR events in the WT strain. GCR events were mapped by multiplex PCR (see Fig. S1 in the supplemental material) to one of the three regions indicated in panel A. The type of event (telomere addition or “other”) was determined by Southern blotting. A total of 29 events were analyzed. The enrichment of GCR events within the 84-bp SiRTA relative to the expected frequency (assuming a random distribution of GCR events across the 11.5-kb target region) was significant by Fisher's exact test (P < 0.001). (C) Schematic of the chromosome V HO-inducible GCR assay system. Expression of the HO endonuclease is induced by growth on medium containing galactose, and the site of HO cleavage is indicated (arrow). (D) Distribution of HO endonuclease-induced GCR events in the WT strain. Data are from three independent experiments and ∼30 to 40 GCRs per experiment. Error bars represent standard deviations.