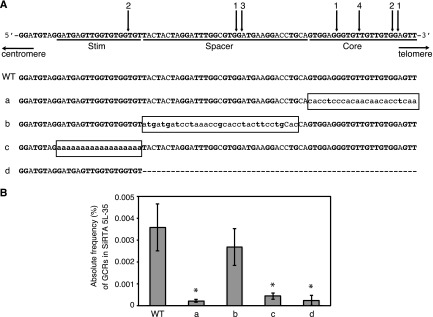
FIG 2.
High rates of telomere addition at SiRTA 5L-35 require two separable sequences. (A) Top schematic, sequence of SiRTA 5L-35 with arrows indicating sites of de novo telomere addition. The most 3′ chromosomal nucleotide with identity to the cloned de novo telomere is indicated. Individual cloned sequences are shown in Fig. S4 in the supplemental material. Numbers above arrows indicate the number of independent telomere addition events mapped to each site. Stim, Spacer, and Core are defined in the text. Bottom schematic, mutations created in SiRTA 5L-35. Uppercase letters represent unchanged nucleotides, lowercase letters enclosed in box represent mutated nucleotides, and the dashed line indicates deleted nucleotides. (B) Core and Stim sequences contribute to the formation of GCR events within SiRTA 5L-35. The frequency (%) at which GCR events occur within SiRTA 5L-35 following induction of HO endonuclease expression on medium containing galactose is shown for the WT strain and for the mutant strains as depicted in panel A. Averages from three independent replicates are shown with standard deviations. Mutants marked with an asterisk are significantly different from WT (P < 0.05) by analysis of variance (ANOVA) with post hoc Tukey's honestly significant difference (HSD).