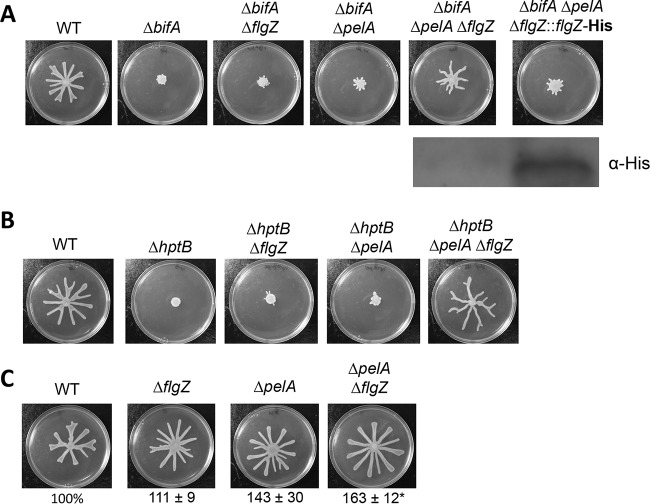
FIG 1.
FlgZ and Pel polysaccharide contribute to swarming motility repression. (A) Top panel: representative swarm plates of the indicated strains. Bottom panel: Western blot probed with anti-His antibody to detect FlgZ-His expression in the ΔbifA ΔpelA ΔflgZ::flgZ-His strain in which the flgZ gene deletion is complemented by allelic replacement, resulting in expression of a His epitope-tagged FlgZ protein. (B) Representative swarm plates of the indicated strains. (C) Representative swarm plates of the indicated strains. The values below the swarm plates indicate the percentages (means ± standard errors of the means [SEM] of the results determined in three independent experiments performed with six plates each) of plate surface coverage of the mutant strains relative to that of the WT strain (set at 100%). Significance was determined by analysis of variance and Dunnett's posttest comparison for differences relative to the WT. *, P < 0.05 (compared to WT).