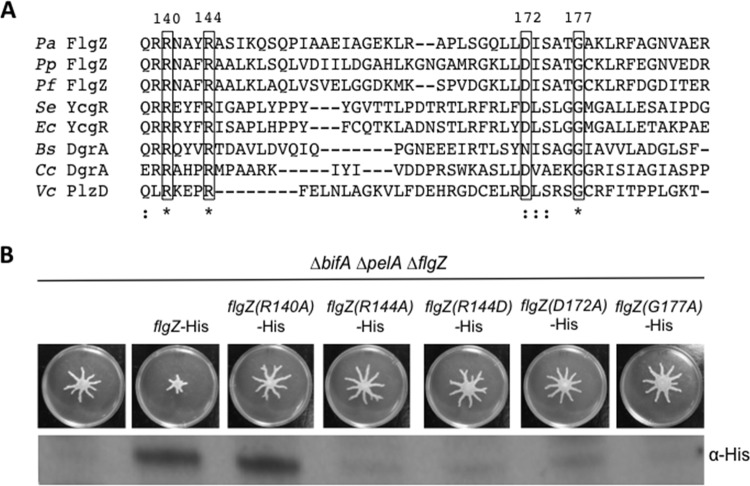
FIG 2.
Conserved residues in the c-di-GMP binding domain are important for FlgZ stability and function. (A) Multiple-sequence alignment of the predicted c-di-GMP binding region of FlgZ in P. aeruginosa (Pa) with orthologs from P. putida (Pp), P. fluorescens (Pf), S. enterica (Se), E. coli (Ec), and B. subtilis (Bs) along with other PilZ domain-containing proteins from C. crescentus (Cc) and V. cholerae (Vc). The sequence alignment was generated by Clustal Omega (59, 60) using the complete PilZ domain of each protein as predicted by SMART (61, 62). A portion of the alignment is shown here. Clustal Omega determined conservation of residues. ★, a fully conserved residue; :, a residue with strongly similar properties. The boxed conserved residues were targeted for site-directed mutagenesis. Numbers correspond to the amino acid residues in the P. aeruginosa FlgZ full-length protein. (B) Top panel: representative swarm assays of the indicated strains. Bottom panel: protein levels determined using Western blotting and anti-His antibody to detect expression of the wild-type strain and mutant FlgZ-His variants.