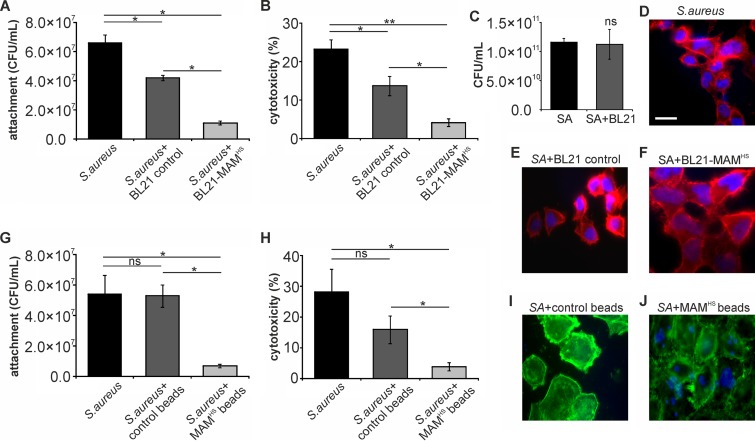
FIG 6.
The inhibitory effect of BL21+MAMHS on Staphylococcus aureus (SA) is due to a combination of attachment competition and interspecies antagonism. HeLa cells were infected with S. aureus (MOI, 10) alone or in the presence of either the BL21 control or the BL21+MAMHS strain. Alternatively, HeLa cells were infected with S. aureus (MOI, 10) alone or in the presence of either GST-coupled control beads or MAMHS-coupled beads. After 4 h, the numbers of attached S. aureus cells were determined by selective plating (A, G) and cytotoxicity toward HeLa cells was determined by LDH release assays (B, H). Cytotoxicity was normalized against that for uninfected (0%) and Triton X-100-lysed (100%) samples. The morphology of infected HeLa cells following infections was determined by imaging. The staining in panels D to F shows DNA (blue) and F-actin (red). Bar, 20 μm. The staining in panels I and J shows the beads (blue) and F-actin (green). (C) Mixed planktonic cultures of S. aureus and BL21 were grown for 4 h, and the number of S. aureus cells was determined by selective plating. Results are means ± SEMs (n = 3), and significance was determined using Student's two-tailed t test on raw data. *, P ≤ 0.05; **, P ≤ 0.01; ns, no significant difference.