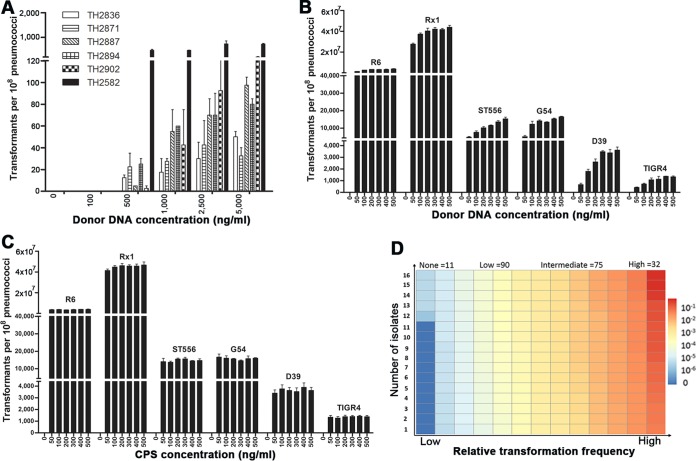
FIG 1.
Diversity of S. pneumoniae isolates in natural transformability. The impact of donor DNA concentration on natural transformability of the six initially nontransformable isolates (A) or common laboratory strains (B) was determined as described in Materials and Methods. (C) A similar approach was used to assess potential dose effect of the CSP on transformability of the selected laboratory strains. The values represent the numbers of transformants for each strain (per ∼108 cells) ± standard errors from three replicates in the presence of various concentrations of donor DNA (in panels A and B) or CSP (in panel C). (D) The transformation levels of the 208 pneumococcal isolates were similarly determined in the presence of donor DNA (rpsL1 amplicon, 500 ng/ml) and CSP (500 ng/ml) and are indicated by colors as follows: none (RTF = 0, dark blue), low (0.001 ≥ RTF > 0, light blue-light yellow), intermediate (0.03 ≥ RTF > 0.001, yellow-orange), and high (RTF > 0.03, dark orange-red). Each rectangle represents a strain. The relative transformation frequency (RTF) value of each isolate was calculated by dividing its transformants with that of strain R6. The number of strains in each transformability category is indicated at the top. The transformation frequency and associated information of the isolates are described in Table S1 in the supplemental material.