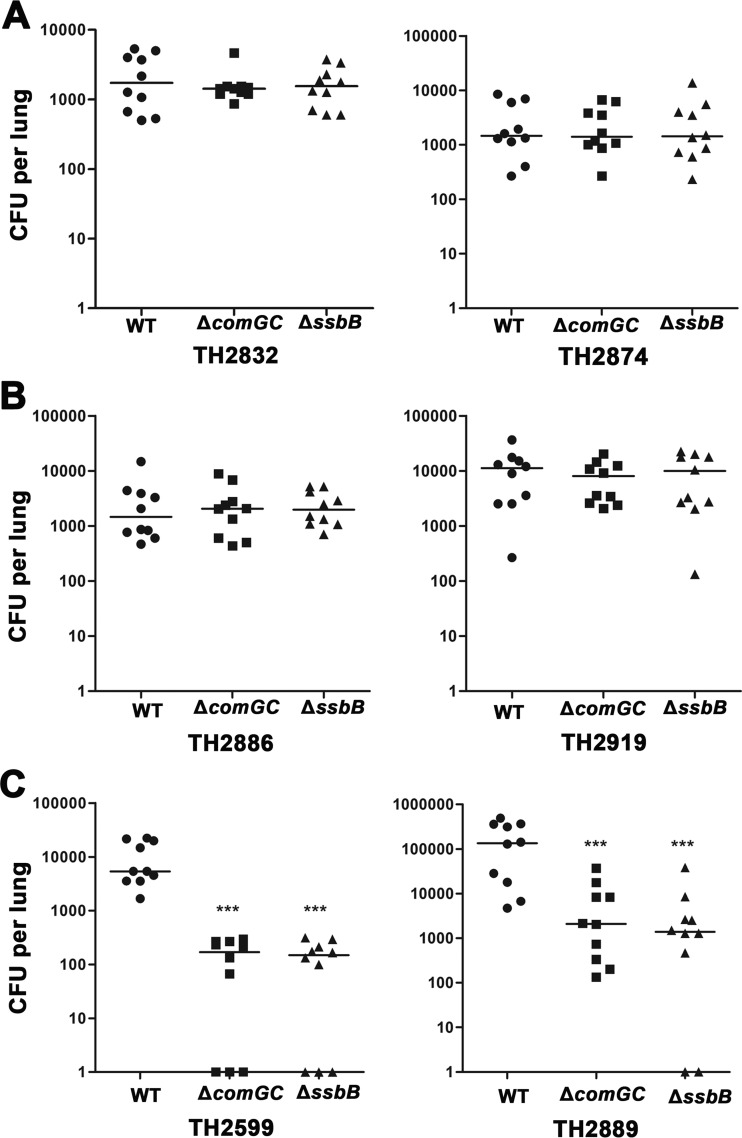
FIG 6.
Significant attenuation of the ΔcomGC and ΔssbB mutants in the hypertransformable pneumococcal backgrounds in a single-strain infection mouse model of acute pneumonia. The impact of natural transformation on pneumococcal virulence was evaluated with the ΔcomGC and ΔssbB mutants of two selected isolates with low (A)-, intermediate (B)-, or high (C)-transformability phenotype in a single-strain infection mouse model of acute pneumonia. Each CD1 mouse was intranasally infected with either the wild type (WT) or an isogenic mutant lacking comGC or ssbB (essential genes for natural transformation) and then sacrificed to quantify the bacterial burden in the lung 48 h later as described in Materials and Methods. Bacterial burden is presented as a CFU value per lung (or mouse); each symbol represents the CFU value of a single mouse. The horizontal bars indicate the medians in individual groups of mice. ***, P < 0.001.