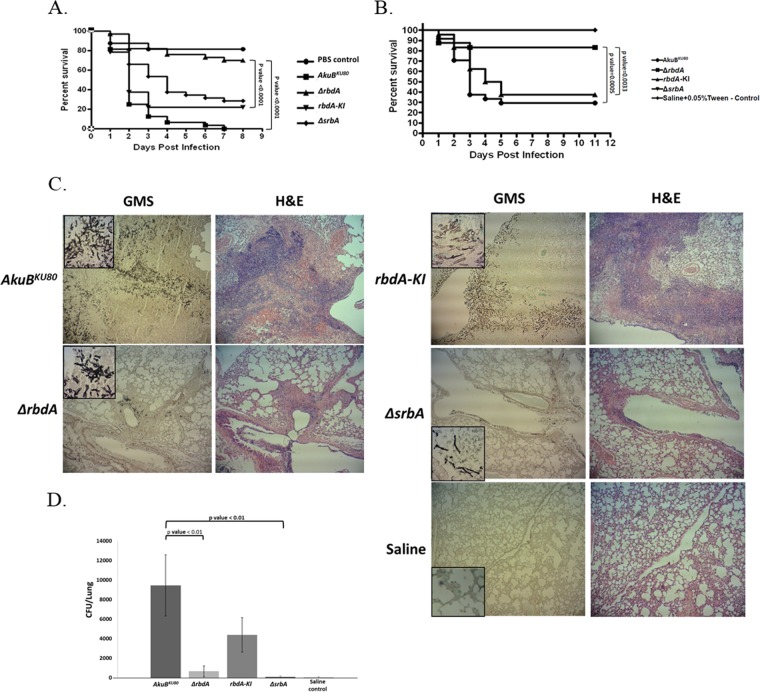
FIG 7.
The ΔrbdA mutant strain exhibits reduced virulence in the Galleria mellonella and murine models of infection. (A) G. mellonella larvae infected with the rbdA-null strain (ΔrbdA) showed a significant increase in their survival rates compared to those infected with the AkuBKU80 background strain or the rbdA-KI reconstituted strain (P < 0.0001, for both). (B) Survival curve of infected, cortisone acetate-immunocompromised mice, infected intranasally with A. fumigatus conidia. Mice infected with the ΔrbdA and ΔsrbA mutant strains showed a significant increase in their survival rates compared to the mice infected with the AkuBKU80 background strain (P = 0.0005) or the rbdA-KI reconstituted strain (P = 0.0033). (C) Mice infected with the ΔrbdA and ΔsrbA mutant strains showed reduced fungal colonization and lung pathology. Mice were infected as described in Materials and Methods. Three days after infection, the mice were sacrificed, and their lungs were removed and sent for histological staining with Grocott's methenamine silver stain (GMS; fungal staining) and hematoxylin and eosin (H&E; tissue and nuclear staining). The infecting ΔrbdA and ΔsrbA mutant strains showed reduced hyphal growth, colony size, tissue damage, and inflammatory cell influx compared to the AkuBKU80 background strain and the rbdA-KI reconstituted strain. (D) Mice infected with the ΔrbdA and ΔsrbA mutant strains showed reduced lung fungal loads. Infected mice were sacrificed on the third day postinfection, their lungs were removed and homogenized, and the homogenates were plated on YAG. The plates were incubated for 16 h, and the numbers of CFU were counted.