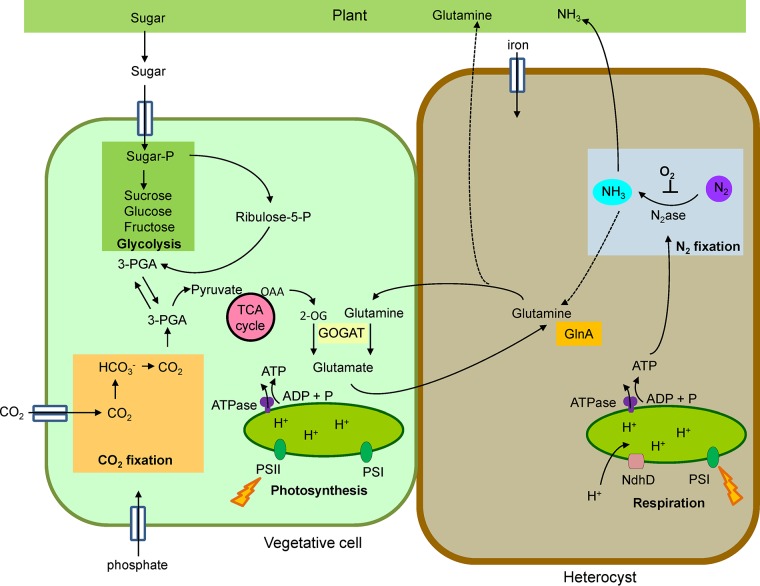
FIG 3.
Schematic illustration of important metabolic pathways in associations of nitrogen-fixing cyanobacteria and host plant. The cell on the left represents a vegetative cell, while the cell on the right represents a nitrogen-fixing heterocyst. Important metabolic pathways in associations of nitrogen-fixing cyanobacteria and host plant are glycolysis, carbon fixation, photosynthesis, respiration, and nitrogen fixation. The nitrogen fixed in the heterocyst is incorporated via the GS-GOGAT pathway and used for the synthesis of amino acids, although during symbiosis, most nitrogen is exported to the plant as NH3. In exchange, sugars are provided by the host plant. GOGAT, glutamate synthase; GlnA, glutamine synthetase; HCO3−, bicarbonate; NH3, ammonia; N2ase, nitrogenase; OAA, oxaloacetate; 3-PGA, polyglycolic acid; PGAL, phosphoglyceraldehyde.