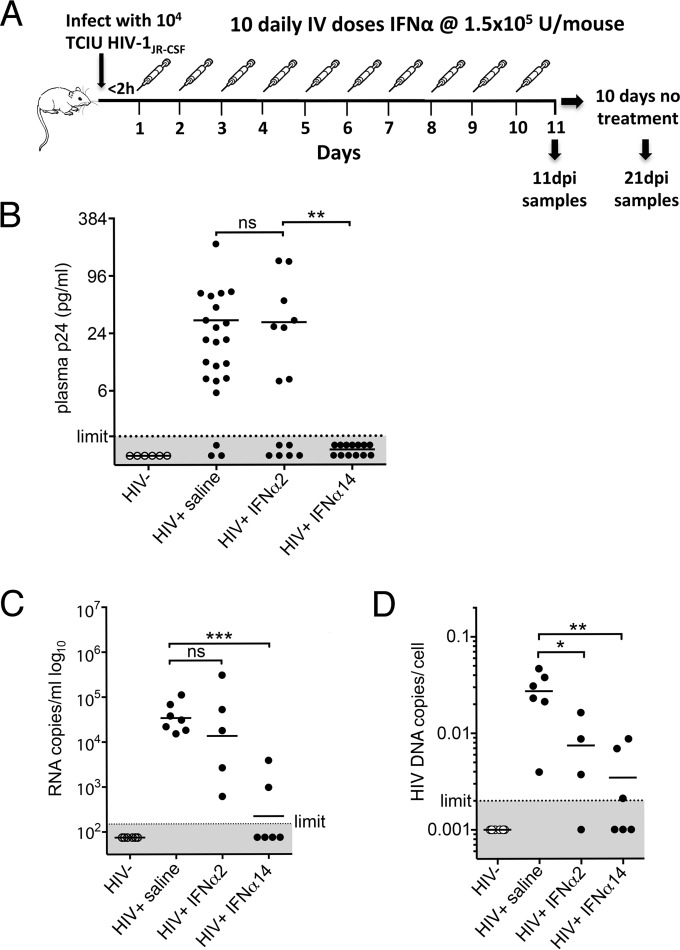
FIG 2.
IFN-α14 suppression of HIV-1 replication in vivo. (A) The in vivo experimental design consisted of intraperitoneal infection of TKO-BLT mice with 104 TCIU of HIV-1JR-CSF, followed by intravenous administration of either IFN-α2, IFN-α14, or mock saline within 2 h of infection. Treatment was administered daily for 10 consecutive days, followed by sample collection either 24 h after the final injection (11 dpi) or after an additional 10-day period of no treatment (21 dpi). (B) HIV-1 p24 levels detected by ELISA in plasma collected from HIV-1JR-CSF-infected TKO-BLT mice 24 h after the final IFN treatment (11 dpi). The dots represent individual mice reconstituted from three separate human donors. The results comparing controls to IFN-α2 and IFN-α2 to IFN-α14 (detectable p24 versus undetectable p24) were analyzed by chi-square analysis with a Bonferroni correction for multiple comparisons (**, P = 0.0019; ns, not significant). (C) HIV-1 RNA copies per milliliter of plasma at 11 dpi, detected by quantitative PCR (qPCR). (D) HIV-1 proviral copies detected in CD4 cell-enriched TKO-BLT splenocytes at 11 dpi. One of the samples from the IFN-α2 group did not provide data, as the PCR was inhibited. (B to D) The horizontal lines denote means. (C and D) Statistical analyses were done by one-way ANOVA with Dunnett's posttest for multiple comparisons. ***, P < 0.001; **, P < 0.01; *, P < 0.05. Each dot represents a separate mouse.