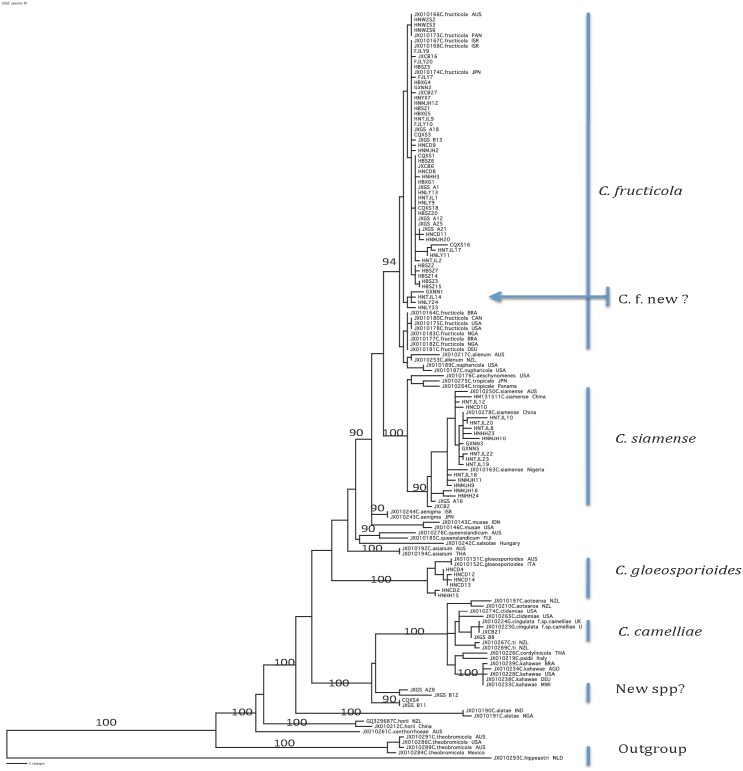
Fig 2. Neighbor-Joining phylogeny showing the relationships among the representative strains of the 85 multilocus genotypes of the Colletotrichum gloeosporioides species complex (CGSC) analyzed in this study and with reference genotypes of 22 phylogenetic species within CGSC.
The phylogeny was obtained by using the concatenated sequences of three loci (ITS, CL and GD) totaling 1362bp. Each reference taxon is represented by the GenBank accession number of its ITS sequence, followed by the species name and the country where the strain was originally isolated. The branch lengths are proportional to the amount of nucleotide sequence divergence. The species that our isolates belonged to were indicated at the right margin: C.f., C. fructicola; C.s., C. siamense; C.g. C. gloeosporioides; C.c., C. camelliae. The four genotypes representing five strains that are not clustered with any of the 22 known phylogenetic species within CGSC are marked by “New spp?”. Similarly, the seven isolates (four genotypes) within C. fructicola that are distinctly different from the remaining 160 C. fructicola isolates are marked by “C.f. new?”. Bootstrap values greater than 90% are shown. The tree was rooted by outgroup taxon C. hippeastri.