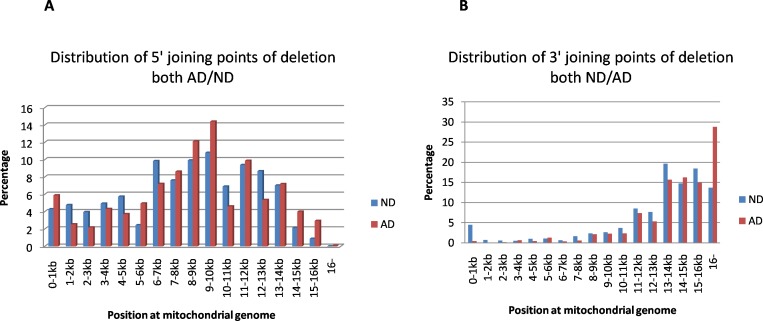
Fig 2. Distribution of 5’ and 3’joining points of deletion both ND and AD.
A. 5’ joining points of deletion: The X-axis represents the nucleotide position along the mitochondrial genome divided into 1kb nucleotide increments, and the Y-axis represents the average percentage deletion part in aging samples (ND) or patients with Alzheimer’s disease (AD). The percentage of regional deletion within each kb is calculated by dividing the total number of deletions (5’ breakpoint) within 1kb by the total deletions in the sample. B. 3’ joining points of deletion: The X-axis represents the nucleotide position along the mitochondrial genome divided into 1kb nucleotide increments, and the Y-axis represents the average deletion part in aging samples (ND) or patients with Alzheimer’s disease (AD). The percentage of regional deletion within each kb is calculated by dividing the total number of deletions (3’ breakpoint) within 1kb by the total deletions in the sample. AD samples have more 3’ breakpoint at 16kb (28.8% in AD compared 13.7% in ND, P = 0.02).