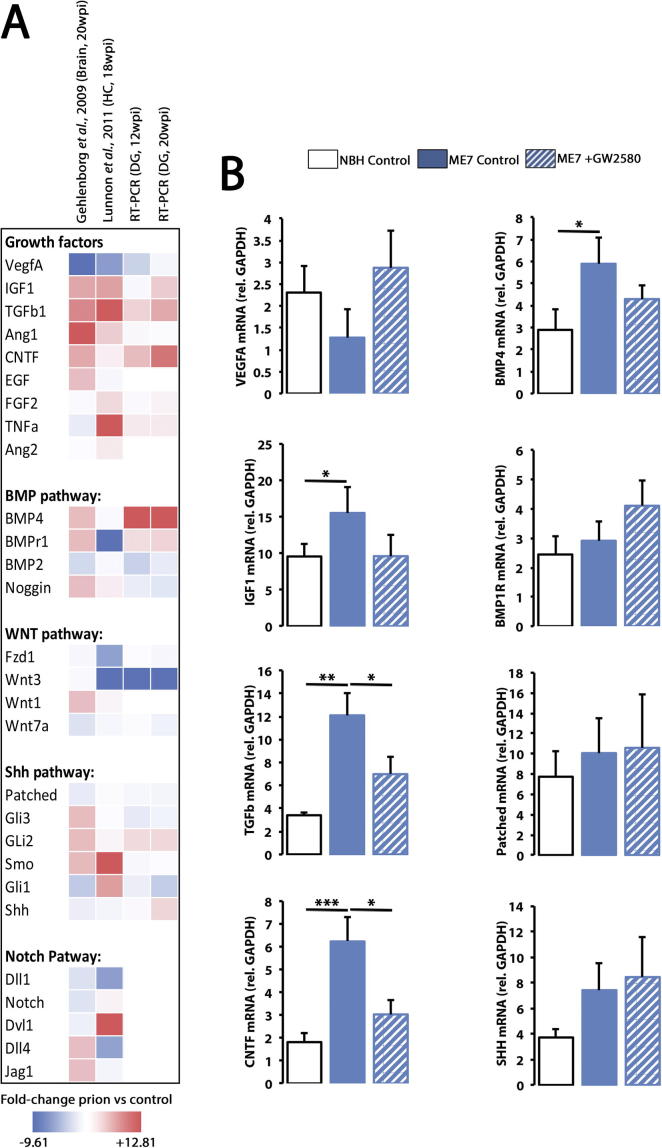
Fig. 5.
Gene expression screening of potential molecules regulating the pro-neurogenic activity of microglia in prion-diseased mice. (A) Progressive screening of gene expression profiles (see methods and Table S1), from microglia related mRNA species reported in two published microarray studies of models of prion disease, using whole brain (Gehlenborg et al., 2009) or hippocampal samples(Lunnon et al., 2011) and RT-PCR analysis in the dentate gyrus (DG) microdissected samples from both NBH (normal brain homogenate) and ME7 mice, at 12 and 20 weeks post-induction. Data shown colour-coding (blue to red) fold-change of prion vs. control from −9.61 to +12.81. (B) The mRNA expression of shortlisted molecular candidates (Patched, Shh, Bmp4, Bmp1r, Tgfβ1, Cntf, Igf1, Vegfa) was analysed by RT-PCR in DG microdissected samples from NBH, ME7 and ME7+GW2580 mice. Expression of mRNA represented as mean ± SEM and indicated as relative expression compared to the housekeeping gene (GAPDH) using the 2−ΔΔCT method. Statistical differences for connected bars: *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. Data were analysed with a one-way ANOVA showing statistical comparisons arising from a post-hoc Tukey test (n = 4).