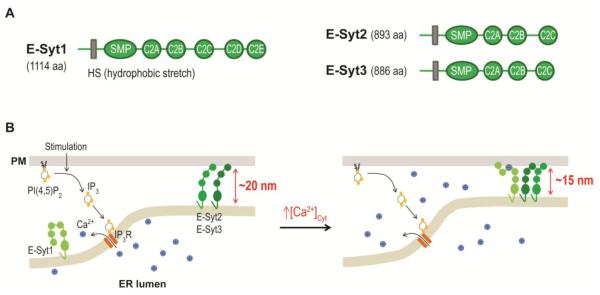
Figure 3.
Regulation of ER-PM junctions by E-Syts.
(A) Diagrams of human E-Syt1, E-Syt2, and E-Syt3 domain structures. HS, hydrophobic stretch; SMP, synaptotagmin-like-mitochondrial-lipid binding protein domain.
(B) E-Syt2 and E-Syt3 provide ER-PM tethering in resting cells. The increase in cytosolic Ca2+ levels during PI(4,5)P2-Ca2+ signaling triggers E-Syt1 translocation to ER-PM junctions, resulting in a reduction in the gap distance.