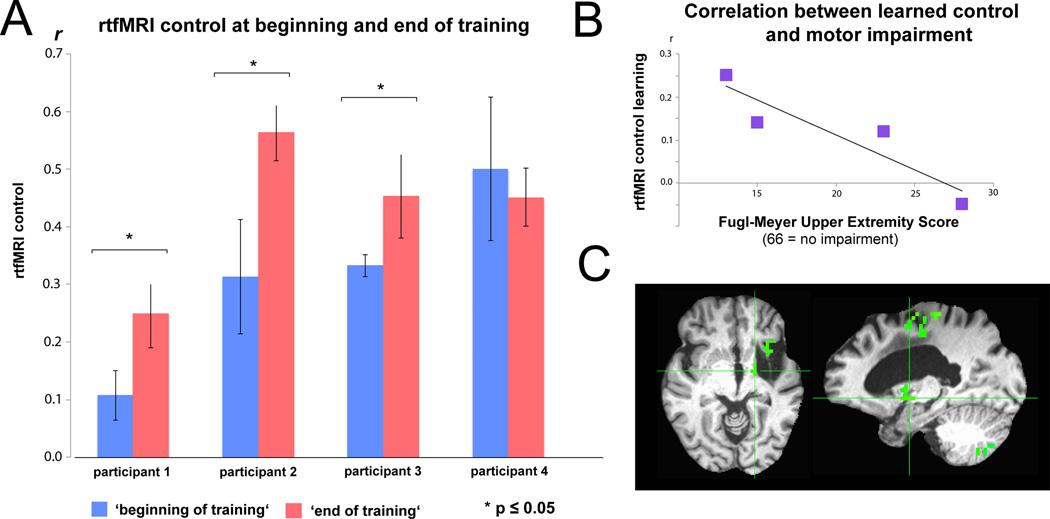
Figure 2.
A: Real-time functional magnetic resonance imaging (rtfMRI) connectivity control at the beginning (first three runs of session 1) and end of training (last three runs on session 2). r = Pearson correlation value of regions of interest’s (ROIs) blood-oxygenation-level-dependent (BOLD) signals. B: Individuals with lower Fugl-Meyer Upper Extremity (F-MUE) scores, reflecting less remaining motor function, showed a trend towards better learning than individuals with higher scores (r = −0.914, p = 0.08). C: Exemplary whole brain analysis showing increased correlated activation between perilesional M1 and ipsilesional thalamic areas at the end of training (cluster-corrected for multiple comparisons, p<0.05).