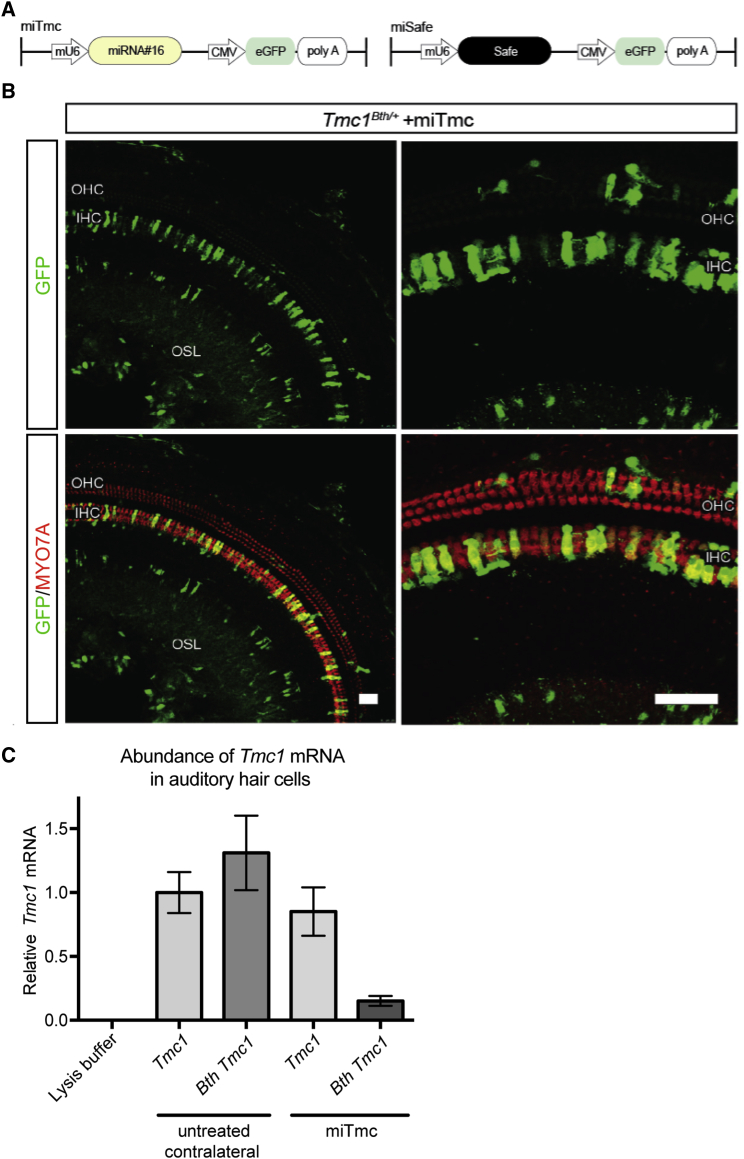
Figure 3.
rAAV2/9-Mediated miTmc Suppresses Expression of Tmc1 c.1235T>A In Vivo
(A) Dual-promoter viral insert in which the U6 promoter drives miTmc miRNA expression and the CMV promoter drives eGFP expression. miSafe was specifically selected for its validated low off-targeting potential.24
(B) Two weeks after trans-RWM injection of miTmc at P0–P2, native eGFP localization was visible in transduced IHCs and OHCs in the organ of Corti.
(C) Expression of wild-type Tmc1 and Bth Tmc1 mRNA was measured by real-time qPCR using allele-specific primers. Allele-specific qPCR amplification was carried out on groups of individually isolated auditory hair cells (Movie S1). All samples were normalized to β-actin. Expression of wild-type Tmc1 mRNA measured in the untreated contralateral sample was set at a value of 1. mRNA abundance was calculated in relation to that of this untreated contralateral sample with wild-type Tmc1. Abundance of both wild-type Tmc1 and Bth Tmc1 were measured in samples containing 12 cells collected from either miTmc-treated ears or untreated contralateral ears from five 4-week-old Tmc1Bth/+ mice. Cells collected from untreated contralateral ears were GFP negative, whereas cells collected from miTmc-injected ears were GFP positive. mRNA abundance was calculated by the ΔΔCt method. The range indicated by the error bars represents the SD of ΔΔCt on the basis of the fold-difference calculation 2−ΔΔCt, where ΔΔCt + S and ΔΔCt − S.