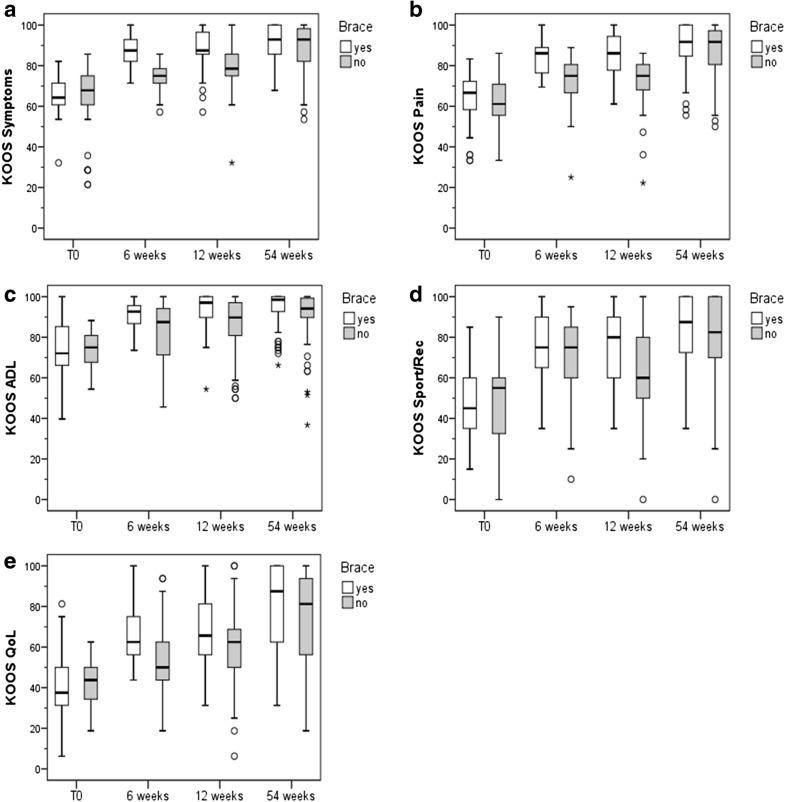
Fig. 4.
Results of the five KOOS subscales. Non-parametric tests were used for all five KOOS subscales (Kolmogorov–Smirnov-test, p < 0.05). a KOOS symptoms: In both groups the KOOS symptoms sub-score increased significantly (Friedman-test, p < 0.001). Significant between-group differences could be detected after 6 (U test, p < 0.001) and 12 (p < 0.001) weeks of intervention. b In both groups the average KOOS pain values increased from T0 to all three follow-up examinations (Friedman-test, p < 0.001). Significant between-group differences could be detected after 6 (U test, p < 0.001) and 12 weeks (p < 0.001) of intervention. c In both groups, the KOOS ADL sub-score increased over all time points (Friedman-test, p < 0.001). Significant between-group differences could be detected after 6 (U test, p = 0.002), 12 (p < 0.001) and 54 weeks (p = 0.034) of intervention. d In both groups, the KOOS sports/rec sub-score increased over all follow-up time points (Friedman-test, p < 0.001). Significant between-group differences could be detected after 6 (U test, p = 0.038) and 12 (p = 0.001) weeks of intervention. e In both groups, the KOOS QoL sub-score increased over all follow-up time points (Friedman-test, p < 0.001). Significant between-group differences could be detected after 6 (U test, p = 0.001) and 12 (p = 0.011) weeks of intervention