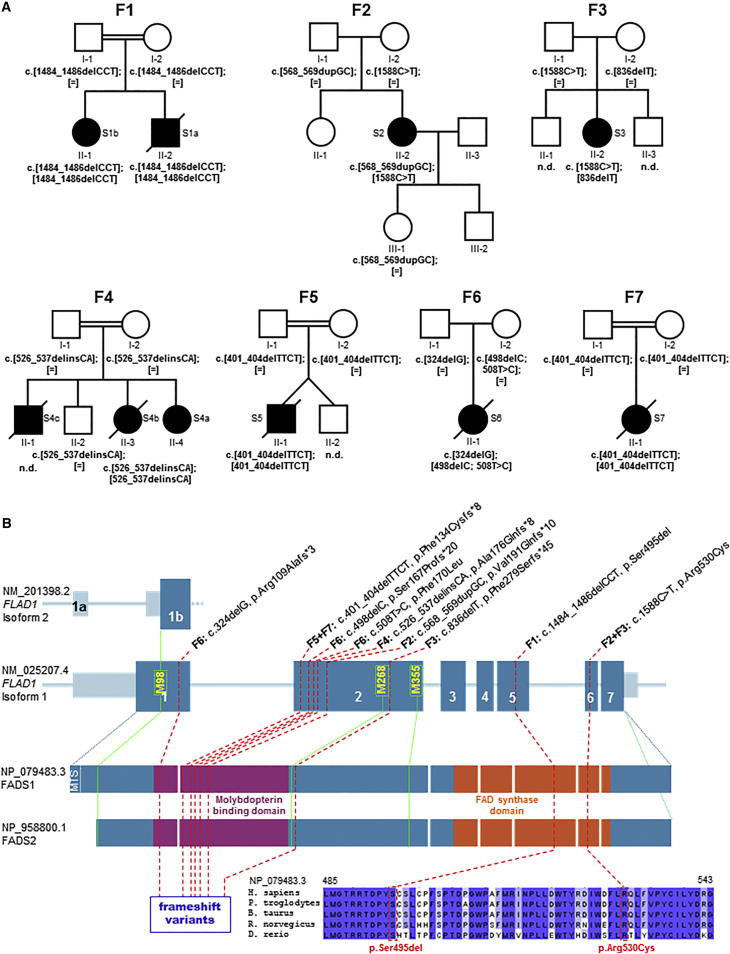
Figure 1.
FLAD1 Variants and Gene and Protein Structure
(A) Pedigrees of the investigated families (F1–F7) with recessively inherited FLAD1 variants. Affected individuals are indicated by closed symbols.
(B) Gene structure with exons and introns shows the localization of the investigated gene variations (homozygous variants are underlined). Met residues located upstream of the FADS domain are presented in yellow with their corresponding protein positions with respect to isoform 1 (GenBank: NM_025207.4). Isoforms 1 and 2 are reported in the UCSC Genome Browser as transcripts possessing an intact and active FADS domain. The protein structure highlights the MPTb domain in violet and the FADS domain in orange. Protein consequences of the identified FLAD1 mutations include the frameshift variants located in the MPTb domain and the two amino acid changes in a region of the FADS domain, which is highly conserved among eukaryotic species. Amino acid residues that are conserved across all species are highlighted in dark blue.