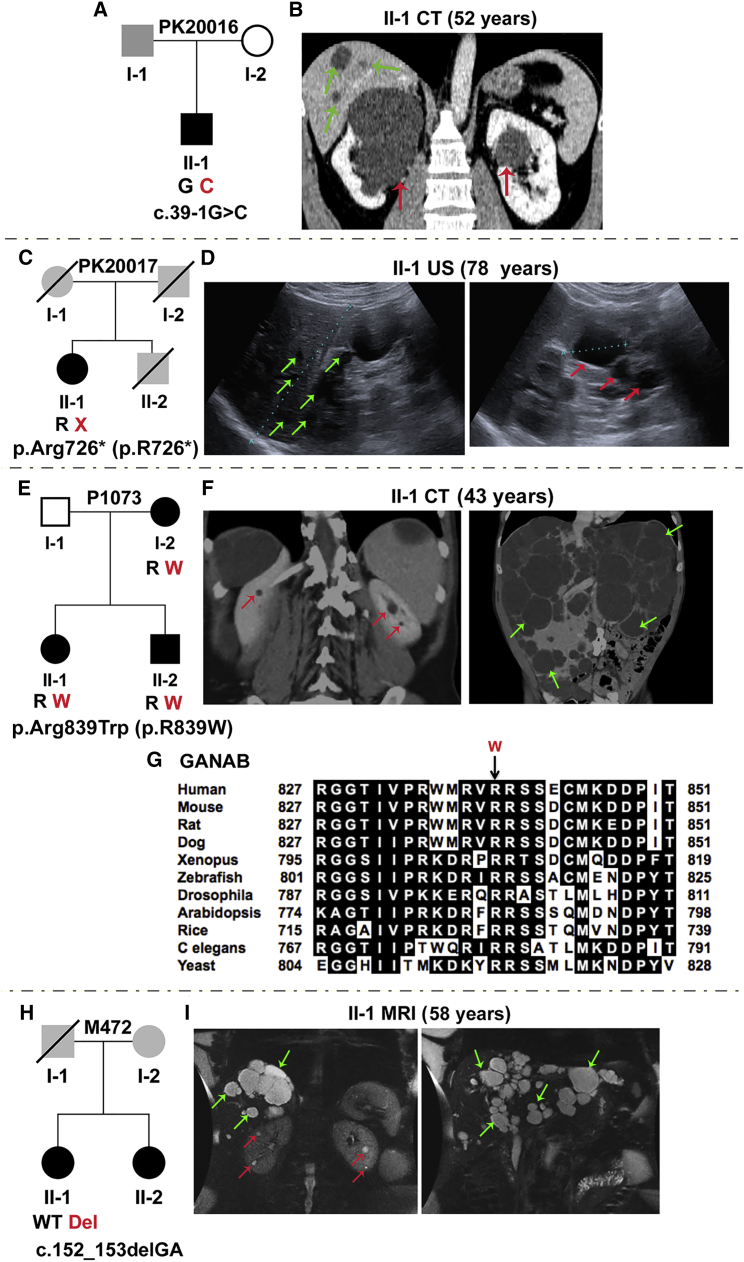
Figure 3.
Characterization of GANAB Variants in Four Families, Including ADPLD-Affected P1073 and M472
(A) Pedigree of family PK20016 shows the splicing mutation c.39−1G>C (IVS1). The family history is unclear because samples were unavailable, but one large renal cyst was reported in I-1.
(B) CT scan of II-1 shows bilateral kidney cysts and occasional hepatic cysts.
(C) Pedigree of family PK20017 shows p.Arg726∗ (p.R726∗) (c.2176C>T, exon 18), in the proband, II-1. A lack of DNA samples and clinical information precluded determining the family history. II-2 died at 55 years from a ruptured intracranial aneurysm, but his PKD status was unknown.
(D) Ultrasound examination of II-1 shows several liver (left), and kidney cysts (right).
(E) Pedigree of family P1073 shows p.Arg839Trp (p.R839W) (c.2515C>T, exon 22) in three affected individuals.
(F) CT scan of II-1 shows very few kidney cysts (left) but severe PLD (right). Gross images of the liver of this subject have been published.57
(G) MSA of GANAB (GIIα) orthologs shows invariant conservation of Arg839 across species. In silico mutation analysis highly predicts p.Arg839Trp (p.R839W) to be pathogenic (SIFT = 0.00, Align GVGD = C65).
(H) Pedigree of family M472 shows c.152_153delGA (p.Arg51Lysfs∗21) (p.R51fs; exon 3) in II-1.
(I) MRI of II-1 shows a few renal cysts (left) but significant PLD; this image was subsequent to earlier resections (Table 1). No sample was available from II-2, but imaging also showed predominant PLD (Figure S3E). Unavailable parental DNA samples and limited clinical information precluded determining the family history, but I-1 was reported to have had a cerebral hemorrhage. Red and green arrows indicate kidney and liver cysts, respectively. Where multiple cysts are present, only representative cysts are highlighted.