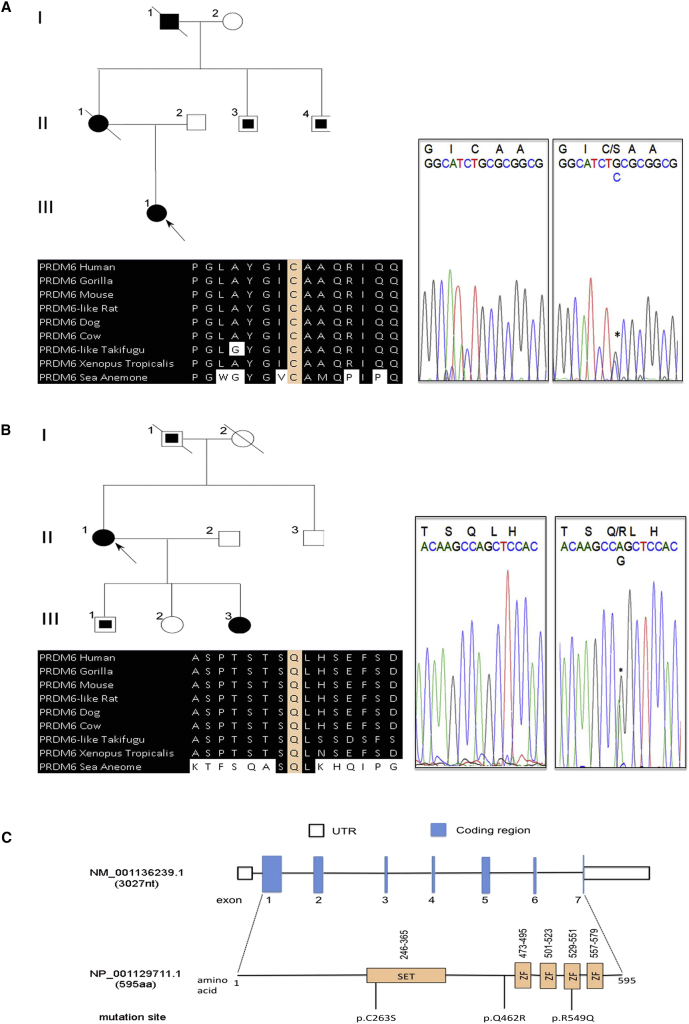
Figure 2.
Independent Non-conservative Mutations of PRDM6 in Subjects with PDA
(A and B) A pedigree with a DNA segment flanking the PRDM6 c.788G>C mutation (resulting in p.Cys263Ser) and a portion of the protein flanking Cys263 in diverse vertebrate species are shown in (A). A pedigree with a DNA segment flanking the PRDM6 c.1385A>G mutation (resulting in p.Arg549Gln) and a portion of the protein flanking Gln462 in diverse vertebrate species are shown in (B). Individuals with PDA are indicated by black symbols, individuals without PDA are shown as unfilled symbols, and individuals with unknown PDA status are shown with partially filled squares. Circles represent females, squares represent males, and symbols with a slash through them indicate deceased subjects.
(C) A schematic of PRDM6 with functional domains and the location of the three independent mutations are shown. Intronic regions are not drawn to scale. ZF denotes zinc finger.