Figure 4.
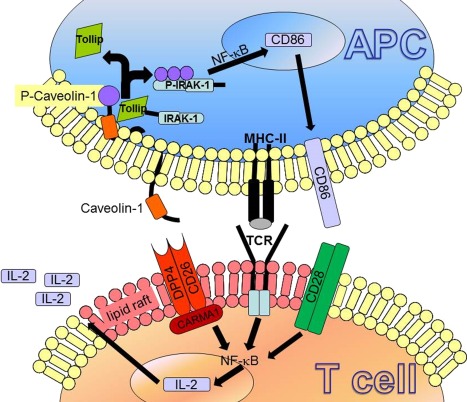
A model of CD26 interacting with caveolin‐1 resulting in T cell co‐stimulation and activation as proposed by Ohnuma et al. 188: after antigen uptake via caveolae by antigen‐presenting cells (APCs), caveolin‐1 is exposed on the cell surface and aggregates in the immunological synaps in lipid rafts. Consequently, caveolin‐1 binds to CD26 and is phosphorylated, leading dissociation of interleukin (IL)−1 receptor‐associated kinase 1 (IRAK‐1) and Tollip. This lead to activation of nuclear factor (NF)‐κB and results in CD86 up‐regulation, supporting the immunological synapse and thus T cell co‐stimulation. In T cells, after caveolin‐1 to CD26 binding, (CARD11) CARMA1 is recruited to the cytosolic portion of CD26. Activation of NF‐κB lead to T cell proliferation and IL‐2 production.
