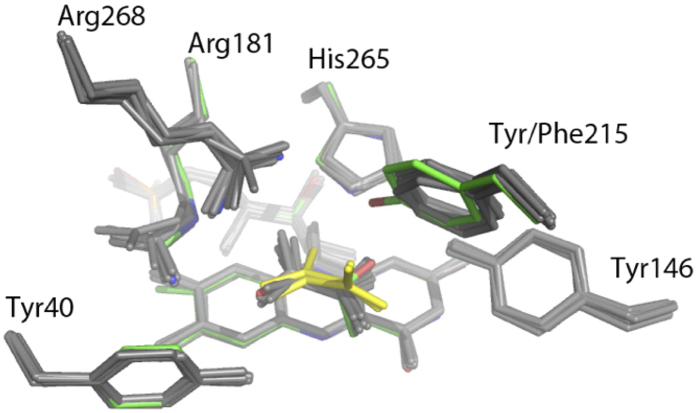
Figure 6. Superpositioning of the active sites from a wild-type monomer (colored by atom type) and the eight subunits from the Y215F mutant (grey) is shown.
The pyruvates from the Y215F mutant subunits with an open lid (yellow) show that lid residues including Tyr215 constrain the binding of the pyruvate. The ring at the site of the mutation is slightly but consistently shifted from the conformation of the wild-type enzyme. This has the effect of substituting a van der Waals interaction between the phenyl group of Phe215 and the pyruvate methyl for a weak hydrogen bond between Tyr215 and the carbonyl oxygen in the wild-type enzyme.