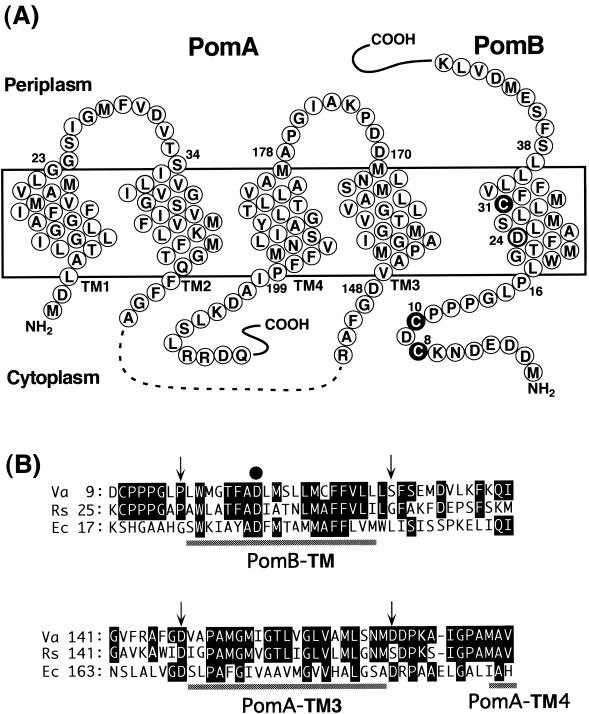
FIG. 1.
Putative membrane topology of PomA and PomB and sites of mutations used in this study. (A) The predicted structure of PomA (left) is taken from Asai et al. (5). PomA has four TMs, TM1 to TM4, and no Cys residues. PomA has a ca. 100-amino-acid cytoplasmic region (dashes) that plays a critical role in interactions with the rotor protein FliG. Wild-type PomB (right) has three Cys residues, Cys-8, Cys-10, and Cys-31 (white letters in filled circles). The predicted topology of PomB is from Asai et al. (2) and Braun and Blair (14) but modified as described in Discussion. PomB has an essential 24th Asp residue in its TM (bold circle) and a large (length, ∼270 amino acids) C-terminal periplasmic domain (not shown), which contains the putative peptidoglycan-binding region. (B) Alignments of the PomA TM3 and the PomB TM regions with the TM regions of MotA and MotB. Va, V. alginolyticus; Rs, Rhodobacter sphaeroides; Ec, E. coli. Residues that are identical to those of V. alginolyticus are indicated by white letters in black boxes. Arrows indicate cross-linked residues between PomA TM3 and PomB TM. The closed circle indicates the essential Asp residue, which is thought to bind protons or sodium ions.