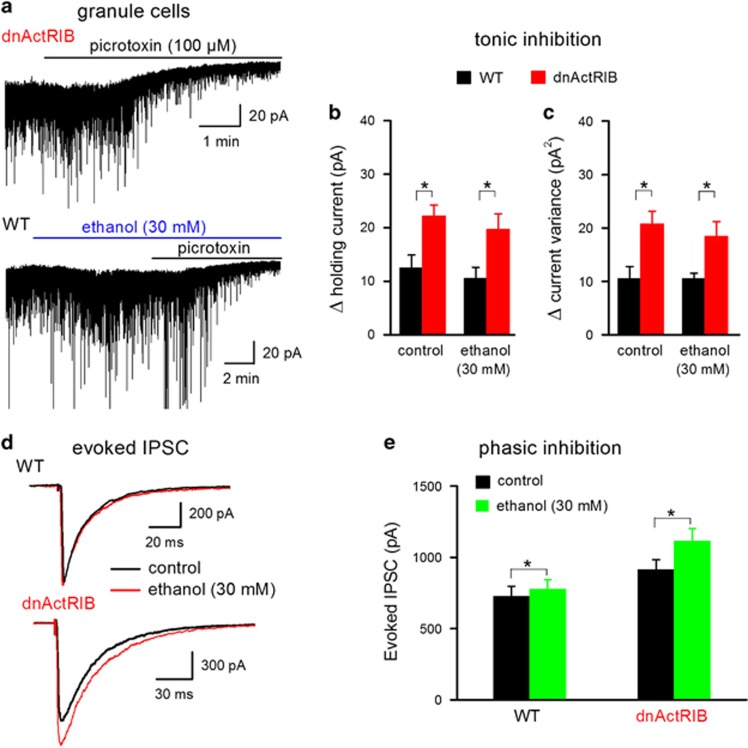
Figure 4.
Differential effect of ethanol on phasic vs tonic inhibition in dentate granule cells. (a) Representative traces illustrate tonic GABA current of a dnActRIB granule cell in the absence of ethanol (upper trace) and of a wt granule cell in the presence of ethanol (30 mM; bottom trace), respectively. (b, c) Histograms summarize enhanced GABAergic tone (expressed as holding current shift and current variance change) in dnActRIB granule cells (wt n=11, dnActRIB n=15) and the lack of effect of low ethanol on tonic inhibition (wt ethanol n=12, dnActRIB ethanol n=9). (d) Superimposed IPSC traces recorded at 35 °C before and during low ethanol (30 mM) from a wt and a dnActRIB granule cell. (e) Histogram summarizes the significantly stronger effects of ethanol on IPSC amplitude in dnActRIB granule cells (wt n=4, dnActRIB n=8). *P<0.05. dnActRIB, dominant-negative activin receptor IB mutant; IPSC, inhibitory postsynaptic currents; wt, wild type.