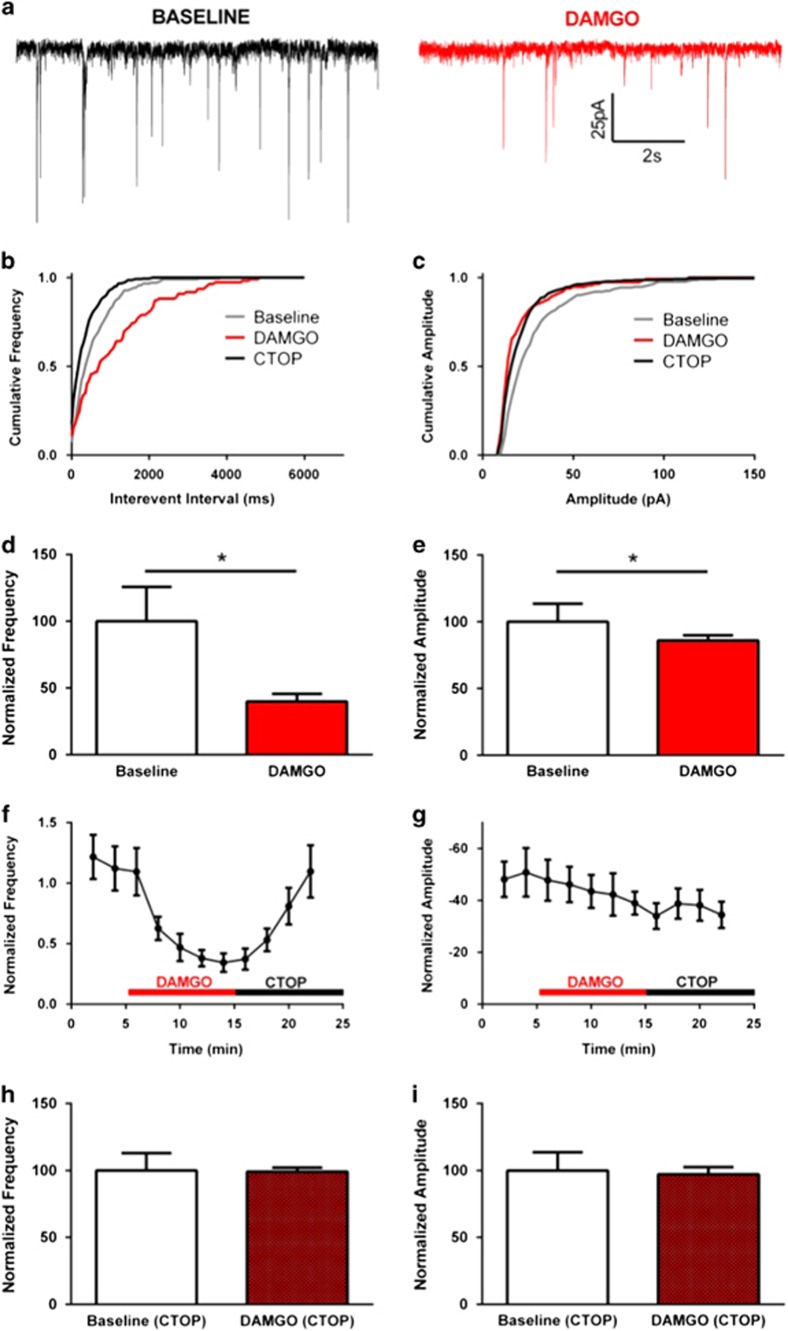
Figure 2.
Mu opioid receptor (MOR) activation reduced mini inhibitory postsynaptic current (mIPSC) in the ventral periaqueductal gray/dorsal raphe (vPAG/DR) dopamine neurons. (a) Representative baseline and post-drug traces demonstrating the effect of [D-Ala2, NMe-Phe4, Gly-ol5]-enkephalin (DAMGO) on mIPSC in the vPAG/DR dopamine neurons. (b, c) Cumulative probability distribution of frequency (b) and peak amplitude (c) before application of DAMGO and followed by D-Phe-Cys-Tyr-D-Trp-Orn-Thr-Pen-Thr-NH2 (CTOP). (d, e) Group effects (n=10) demonstrating DAMGO significantly reduced both mIPSC frequency (d) and amplitude (e). Time course demonstrating group (n =7) DAMGO effects on frequency were reversed by the MOR antagonist CTOP (f); however, effects on amplitude were not reversed (g). CTOP pretreatment blocked the DAMGO effects on mIPSC frequency (h) and amplitude (i) (n =7). * denotes p<0.05 in two-tailed paired Student's t-test.