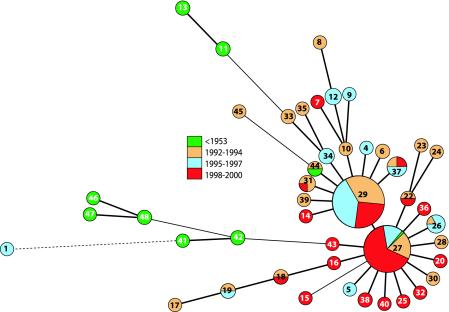
FIG. 1.
Minimum spanning tree of MLVA of Dutch B. pertussis strains. A categorical coefficient and the BURST priority rule of the highest number of single-locus changes were used for the clustering. Each circle in the tree represents a different MLVA type, and the type number is indicated by the number in the circle. Heavy short lines connecting two MLVA types denote types differing by a single MLVA locus, thin longer lines connect double-locus variants, and dotted lines indicate the most likely connection between two types differing by more than two MLVA loci. The connections between types differing in more than a single locus are less likely to represent an evolutionary relationship but indicate the connection to the most similar type. The size of the circle indicates the number of strains with this particular MLVA type; large circles indicate predominant types. The colors indicate the period of time in which the strains included were isolated. If strains isolated from different time periods carry identical MLVA types, pie charts are used to indicate distribution. The predominant MLVA types are types 27 and 29.