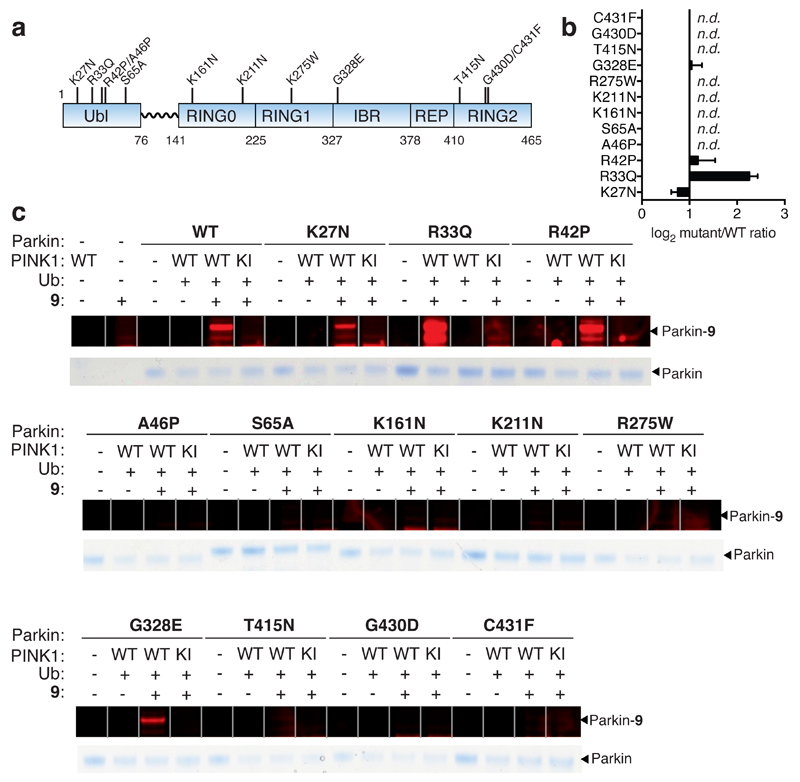
Figure 4. Quantitative and direct activity-based Protein Profiling of transthiolation activity of Parkin patient mutations.
(a) Amino acid boundaries of the multi-domain architecture of Parkin. (b) Fold-change of mutant Parkin transthiolation activity relative to WT represented on a Log2 scale (n.d. means no detectable labeling). Data represent mean values and error bars correspond to ±s.d, n = 3 . (c) Recombinant Parkin mutants were incubated with PhPINK1 in presence of Ub and ATP. Mutations resided throughout the multi-domain architecture of Parkin. Incubations were then directly profiled for Parkin transthiolation activity with fluorescent probe 9 Mutations mildy perturbed, activated or abolished transthiolation activity as determined by fluorescence of labeled Parkin.