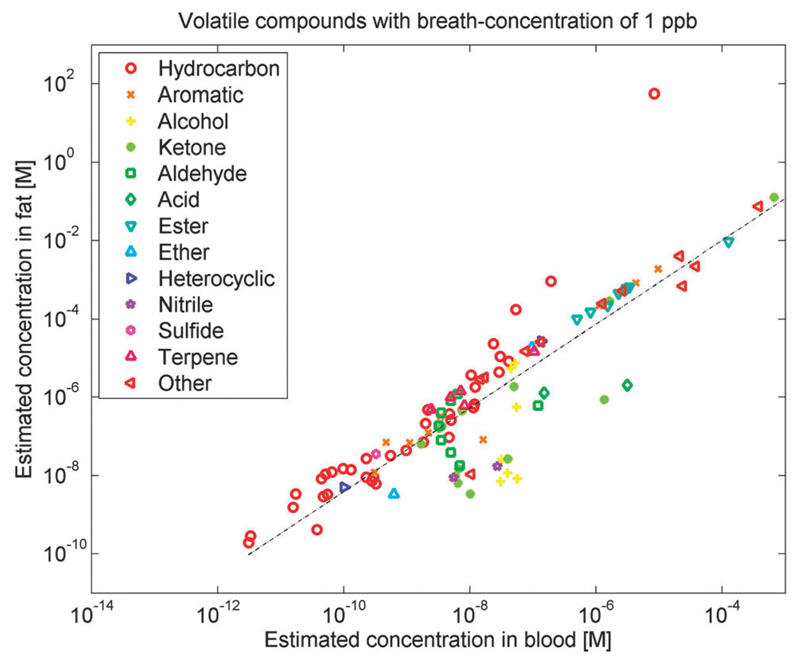
Fig. 3.
Estimated equilibrium concentrations in blood and fat for candidates of volatile cancer biomarkers published during the past decade.4,15,50,56,63,68,71,72,74–76,78,133,202,248,249 These equilibrium concentrations have been estimated under the assumption that the concentration in alveolar breath is 1 part-per-billion (ppb), based on the λb:a (partition coefficient between blood and air) and λf:a (partition coefficient between fat and blood) from Table 1. Hence, for different VOCs showing the same concentration in exhaled breath, the concentration in fat and blood may be very different (up to a factor of 108). Different VOCs, therefore, carry distinctive information on the various compartments of the human body. In the figure, various chemical classes of compounds (such as hydrocarbons or sulfides) are indicated by different symbols and colors.