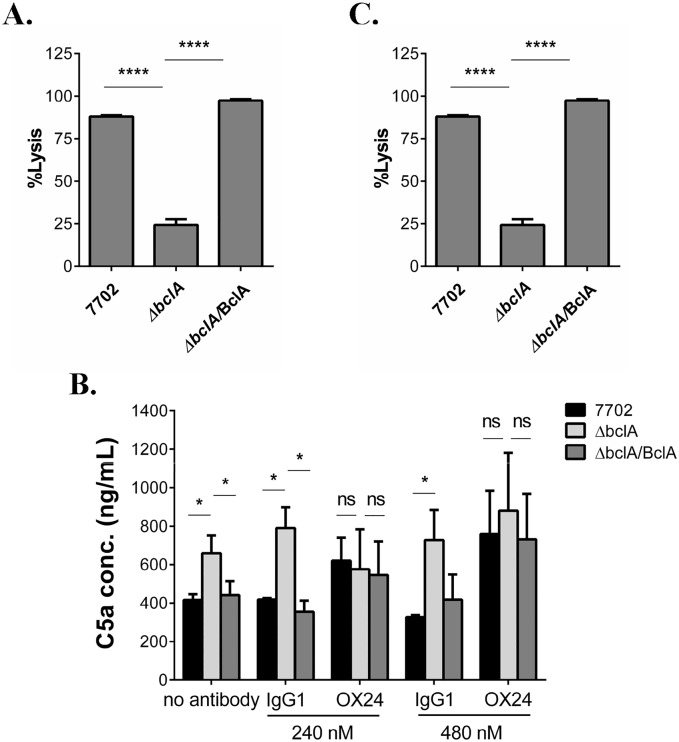
Fig 3. BclA-mediated CFH recruitment inhibited downstream complement activation in vitro and in vivo.
(A) Complement hemolytic assay. Spores were incubated with 20% NHS and centrifuged. The supernatants (1:10 diluted) were used to perform complement hemolytic assays using opsonized sheep erythrocytes (EA-SRBC). Data shown was from at least three independent experiments. (B) Determination of C5a levels in human serum incubated with the different spores. GVB0 buffer containing 20% NHS was pre-treated with buffer only (no antibody), OX24, or control IgG1, followed by incubation with 7702, ΔbclA or ΔbclA/BclA spores. C5a levels in the supernatants were measured using the Human Complement Component C5a DuoSet. Data shown was combined from two independent experiments, each with duplicate wells. (C) Determination of C5a levels in mouse BAL fluid. C57BL/6 were i.n. inoculated with 7702 (n = 8), ΔbclA (n = 8), ΔbclA/BclA (n = 8) spores or PBS (n = 6). BAL fluids were collected 6 hours later and C5a level in the supernatant determined using the Mouse Complement Component C5a DuoSet. Data shown were combined from two independent experiments, each with duplicate wells. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01. ****, p < 0.0001, t test.