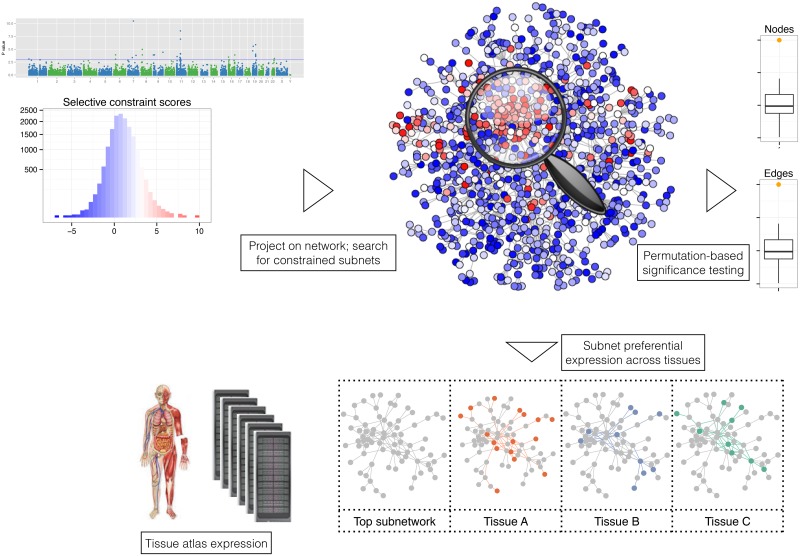
Fig 1. the Protein Interaction Network Tissue Search (PINTS) workflow.
We project gene-wise selective constraint scores [6] onto the InWeb protein-protein interaction dataset [16] and use a heuristic version of the prize-collecting Steiner Tree algorithm [17,29] to detect clusters of interacting constrained genes. We assess significance empirically, by randomly assigning the scores to genes 1000 times and calibrating detected subnetwork parameters. We then test any significant subnetwork for usual patterns of preferential expression [32] across the Roadmap Epigenome Project expression data [14], a cosmopolitan tissue atlas, using a Markov random field approach. The approach is flexible and modular, so gene interaction and tissue expression reference datasets can be altered according to the application.